ATM deficiency results in accumulation of DNA-topoisomerase I covalent intermediates in neural cells
- PMID: 23626666
- PMCID: PMC3634035
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058239
ATM deficiency results in accumulation of DNA-topoisomerase I covalent intermediates in neural cells
Abstract
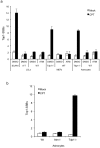
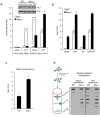
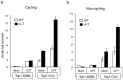
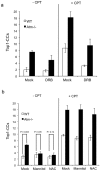
Accumulation of peptide-linked DNA breaks contributes to neurodegeration in humans. This is typified by defects in tyrosyl DNA phosphodiesterase 1 (TDP1) and human hereditary ataxia. TDP1 primarily operates at single-strand breaks (SSBs) created by oxidative stress or by collision of transcription machinery with topoisomerase I intermediates (Top1-CCs). Cellular and cell-free studies have shown that Top1 at stalled Top1-CCs is first degraded to a small peptide resulting in Top1-SSBs, which are the primary substrates for TDP1. Here we established an assay to directly compare Top1-SSBs and Top1-CCs. We subsequently employed this assay to reveal an increased steady state level of Top1-CCs in neural cells lacking Atm; the protein mutated in ataxia telangiectasia. Our data suggest that the accumulation of endogenous Top1-CCs in Atm-/- neural cells is primarily due to elevated levels of reactive oxygen species. Biochemical purification of Top1-CCs from neural cell extract and the use of Top1 poisons further confirmed a role for Atm during the formation/resolution of Top1-CCs. Finally, we report that global transcription is reduced in Atm-/- neural cells and fails to recover to normal levels following Top1-mediated DNA damage. Together, these data identify a distinct role for ATM during the formation/resolution of neural Top1-CCs and suggest that their accumulation contributes to the neuropathology of ataxia telangiectasia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Pommier Y, Redon C, Rao VA, Seiler JA, Sordet O, et al. (2003) Repair of and checkpoint response to topoisomerase I-mediated DNA damage. Mutat Res 532: 173–203. - PubMed
-
- Pourquier P, Pilon AA, Kohlhagen G, Mazumder A, Sharma A, et al. (1997) Trapping of mammalian topoisomerase I and recombinations induced by damaged DNA containing nicks or gaps. Importance of DNA end phosphorylation and camptothecin effects. J Biol Chem 272: 26441–26447. - PubMed
-
- Takashima H, Boerkoel CF, John J, Saifi GM, Salih MAM, et al. (2002) Mutation of TDP1, encoding a topoisomerase I–dependent DNA damage repair enzyme, in spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy. Nat Genet 32: 267–272. - PubMed
-
- Biton S, Dar I, Mittelman L, Pereg Y, Barzilai A, et al. (2006) Nuclear ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) mediates the cellular response to DNA double strand breaks in human neuron-like cells. J Biol Chem 281: 17482–17491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

