The cytokine ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) activates hypothalamic urocortin-expressing neurons both in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 23626705
- PMCID: PMC3633986
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061616
The cytokine ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) activates hypothalamic urocortin-expressing neurons both in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
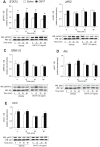
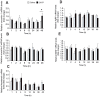
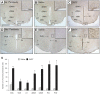
Ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) induces neurogenesis, reduces feeding, and induces weight loss. However, the central mechanisms by which CNTF acts are vague. We employed the mHypoE-20/2 line that endogenously expresses the CNTF receptor to examine the direct effects of CNTF on mRNA levels of urocortin-1, urocortin-2, agouti-related peptide, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and neurotensin. We found that treatment of 10 ng/ml CNTF significantly increased only urocortin-1 mRNA by 1.84-fold at 48 h. We then performed intracerebroventricular injections of 0.5 mg/mL CNTF into mice, and examined its effects on urocortin-1 neurons post-exposure. Through double-label immunohistochemistry using specific antibodies against c-Fos and urocortin-1, we showed that central CNTF administration significantly activated urocortin-1 neurons in specific areas of the hypothalamus. Taken together, our studies point to a potential role for CNTF in regulating hypothalamic urocortin-1-expressing neurons to mediate its recognized effects on energy homeostasis, neuronal proliferaton/survival, and/or neurogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Sleeman MW, Anderson KD, Lambert PD, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ (2000) The ciliary neurotrophic factor and its receptor, CNTFR alpha. Pharm Acta Helv 74: 265–272. - PubMed
-
- Kokoeva MV, Yin H, Flier JS (2005) Neurogenesis in the hypothalamus of adult mice: potential role in energy balance. Science 310: 679–683. - PubMed
-
- Ettinger MP, Littlejohn TW, Schwartz SL, Weiss SR, McIlwain HH, et al. (2003) Recombinant variant of ciliary neurotrophic factor for weight loss in obese adults: a randomized, dose-ranging study. Jama 289: 1826–1832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

