Role of tachykinin 1 and 4 gene-derived neuropeptides and the neurokinin 1 receptor in adjuvant-induced chronic arthritis of the mouse
- PMID: 23626716
- PMCID: PMC3634005
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061684
Role of tachykinin 1 and 4 gene-derived neuropeptides and the neurokinin 1 receptor in adjuvant-induced chronic arthritis of the mouse
Abstract
Objective: Substance P, encoded by the Tac1 gene, is involved in neurogenic inflammation and hyperalgesia via neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor activation. Its non-neuronal counterpart, hemokinin-1, which is derived from the Tac4 gene, is also a potent NK1 agonist. Although hemokinin-1 has been described as a tachykinin of distinct origin and function compared to SP, its role in inflammatory and pain processes has not yet been elucidated in such detail. In this study, we analysed the involvement of tachykinins derived from the Tac1 and Tac4 genes, as well as the NK1 receptor in chronic arthritis of the mouse.
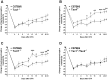
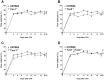
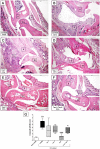
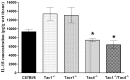
Methods: Complete Freund's Adjuvant was injected intraplantarly and into the tail of Tac1(-/-), Tac4(-/-), Tacr1(-/-) (NK1 receptor deficient) and Tac1(-/-/)Tac4(-/-) mice. Paw volume was measured by plethysmometry and mechanosensitivity using dynamic plantar aesthesiometry over a time period of 21 days. Semiquantitative histopathological scoring and ELISA measurement of IL-1β concentrations of the tibiotarsal joints were performed.
Results: Mechanical hyperalgesia was significantly reduced from day 11 in Tac4(-/-) and Tacr1(-/-) animals, while paw swelling was not altered in any strain. Inflammatory histopathological alterations (synovial swelling, leukocyte infiltration, cartilage destruction, bone damage) and IL-1β concentration in the joint homogenates were significantly smaller in Tac4(-/-) and Tac1(-/-/)Tac4(-/-) mice.
Conclusions: Hemokinin-1, but not substance P increases inflammation and hyperalgesia in the late phase of adjuvant-induced arthritis. While NK1 receptors mediate its antihyperalgesic actions, the involvement of another receptor in histopathological changes and IL-1β production is suggested.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of tachykinins and NK1 receptor in the joint inflammation with collagen type II-specific monoclonal antibody-induced arthritis in mice.J Nippon Med Sch. 2012;79(2):129-38. doi: 10.1272/jnms.79.129. J Nippon Med Sch. 2012. PMID: 22687356
-
Hemokinin-1 mediates anxiolytic and anti-depressant-like actions in mice.Brain Behav Immun. 2017 Jan;59:219-232. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Brain Behav Immun. 2017. PMID: 27621226
-
Hemokinin-1 is an important mediator of pain in mouse models of neuropathic and inflammatory mechanisms.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Apr;147:165-173. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.01.015. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30664920
-
Role of hemokinin-1 in health and disease.Neuropeptides. 2017 Aug;64:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2016.12.003. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Neuropeptides. 2017. PMID: 27993375 Review.
-
Hemokinins and endokinins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004 Jul;61(13):1652-63. doi: 10.1007/s00018-004-4035-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2004. PMID: 15224188 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hemokinin-1 is a mediator of chronic restraint stress-induced pain.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 16;13(1):20030. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46402-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37973885 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental Arthritis Inhibits Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Mice.Cells. 2022 Feb 24;11(5):791. doi: 10.3390/cells11050791. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35269413 Free PMC article.
-
Role of capsaicin-sensitive nerves and tachykinins in mast cell tryptase-induced inflammation of murine knees.Inflamm Res. 2016 Sep;65(9):725-36. doi: 10.1007/s00011-016-0954-x. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Inflamm Res. 2016. PMID: 27251170
-
Tachykinins modulate nociceptive responsiveness and sensitization: In vivo electrical characterization of primary sensory neurons in tachykinin knockout (Tac1 KO) mice.Mol Pain. 2019 Jan-Dec;15:1744806919845750. doi: 10.1177/1744806919845750. Mol Pain. 2019. PMID: 31012376 Free PMC article.
-
Hemokinin-1 induces transcriptomic alterations in pain-related signaling processes in rat primary sensory neurons independent of NK1 tachykinin receptor activation.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Oct 27;16:1186279. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1186279. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37965042 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Nasser AM, Rasker JJ, Valkenburg HA (1997) Epidemiological and clinical aspects relating to the variability of rheumatoid arthritis. Seminars in Arthritis & Rheumatism 27: 123–140. - PubMed
-
- Levine JD, Collier DH, Basbaum AI, Moskowitz MA, Helms CA (1986) Hypothesis: the nervous system may contribute to the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 12: 406–11. - PubMed
-
- Schaible HG, von Banchet GS, Boettger MK, Bräuer R, Gajda M, et al. (2010) The role of proinflammatory cytokines in the generation and maintenance of joint pain. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1193: 60–9. - PubMed
-
- Maggi CA (1995) Tachykinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) as cotransmitters released from peripheral endings of sensory nerves. Prog Neurobiol. 45: 1–98. - PubMed
-
- Szolcsanyi J (1996) Capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerve terminals with local and systemic efferent functions: facts and scopes of an unorthodox neuroregulatory mechanism. Prog Brain Res. 113: 343–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

