Characterization of stratum corneum molecular dynamics by natural-abundance ¹³C solid-state NMR
- PMID: 23626744
- PMCID: PMC3633950
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061889
Characterization of stratum corneum molecular dynamics by natural-abundance ¹³C solid-state NMR
Abstract
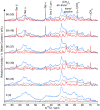
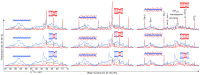
Despite the enormous potential for pharmaceutical applications, there is still a lack of understanding of the molecular details that can contribute to increased permeability of the stratum corneum (SC). To investigate the influence of hydration and heating on the SC, we record the natural-abundance (13)C signal of SC using polarization transfer solid-state NMR methods. Resonance lines from all major SC components are assigned. Comparison of the signal intensities obtained with the INEPT and CP pulse sequences gives information on the molecular dynamics of SC components. The majority of the lipids are rigid at 32°C, and those lipids co-exist with a small pool of mobile lipids. The ratio between mobile and rigid lipids increases with hydration. An abrupt change of keratin filament dynamics occurs at RH = 80-85%, from completely rigid to a structure with rigid backbone and mobile protruding terminals. Heating has a strong effect on the lipid mobility, but only a weak influence on the keratin filaments. The results provide novel molecular insight into how the SC constituents are affected by hydration and heating, and improve the understanding of enhanced SC permeability, which is associated with elevated temperatures and SC hydration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Skin membrane electrical impedance properties under the influence of a varying water gradient.Biophys J. 2013 Jun 18;104(12):2639-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.05.008. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23790372 Free PMC article.
-
Stratum corneum hydration: phase transformations and mobility in stratum corneum, extracted lipids and isolated corneocytes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Nov;1768(11):2647-59. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.05.028. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17927949
-
Skin hydration: interplay between molecular dynamics, structure and water uptake in the stratum corneum.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 16;7(1):15712. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15921-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29146971 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of ceramides and their impact on the stratum corneum structure. Part 2: stratum corneum lipid model systems.Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2008;21(2):58-74. doi: 10.1159/000112956. Epub 2008 Jan 11. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18187965 Review.
-
Stratum Corneum Lipids: Their Role for the Skin Barrier Function in Healthy Subjects and Atopic Dermatitis Patients.Curr Probl Dermatol. 2016;49:8-26. doi: 10.1159/000441540. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Curr Probl Dermatol. 2016. PMID: 26844894 Review.
Cited by
-
Skin hydration dynamics investigated by electrical impedance techniques in vivo and in vitro.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 14;10(1):17218. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73684-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33057021 Free PMC article.
-
Skin membrane electrical impedance properties under the influence of a varying water gradient.Biophys J. 2013 Jun 18;104(12):2639-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.05.008. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23790372 Free PMC article.
-
Probing Skin Barrier Recovery on Molecular Level Following Acute Wounds: An In Vivo/Ex Vivo Study on Pigs.Biomedicines. 2021 Mar 31;9(4):360. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040360. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33807251 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of UVB Irradiation and Oxidative Stress on the Skin Barrier-A New Method to Evaluate Sun Protection Factor Based on Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy.Sensors (Basel). 2019 May 23;19(10):2376. doi: 10.3390/s19102376. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31126113 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mobility in Keratin-Rich Materials Monitored by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: A Tool for the Evaluation of Structure-Giving Properties.Biomacromolecules. 2023 Jun 12;24(6):2661-2673. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.3c00131. Epub 2023 May 18. Biomacromolecules. 2023. PMID: 37199647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scheuplein R, Blank IH (1971) Permeability of skin. Physiol Rev 51: 702–747. - PubMed
-
- Weerheim A, Ponec M (2001) Determination of stratum corneum lipid profile by tape stripping in combination with high-performance thin-layer chromatography. Arch Dermatol Res 293: 191–199. - PubMed
-
- Steinert PM, Marekov LN (1995) The proteins elafin, filaggrin, keratin intermediate filaments, loricrin, and small proline-rich protein-1 and protein-2 are isodipeptide cross-linked components of the human epidermal cornified cell-envelope. J Biol Chem 270: 17702–17711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

