Characterization of stratum corneum molecular dynamics by natural-abundance ¹³C solid-state NMR
- PMID: 23626744
- PMCID: PMC3633950
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061889
Characterization of stratum corneum molecular dynamics by natural-abundance ¹³C solid-state NMR
Abstract
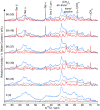
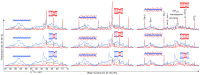
Despite the enormous potential for pharmaceutical applications, there is still a lack of understanding of the molecular details that can contribute to increased permeability of the stratum corneum (SC). To investigate the influence of hydration and heating on the SC, we record the natural-abundance (13)C signal of SC using polarization transfer solid-state NMR methods. Resonance lines from all major SC components are assigned. Comparison of the signal intensities obtained with the INEPT and CP pulse sequences gives information on the molecular dynamics of SC components. The majority of the lipids are rigid at 32°C, and those lipids co-exist with a small pool of mobile lipids. The ratio between mobile and rigid lipids increases with hydration. An abrupt change of keratin filament dynamics occurs at RH = 80-85%, from completely rigid to a structure with rigid backbone and mobile protruding terminals. Heating has a strong effect on the lipid mobility, but only a weak influence on the keratin filaments. The results provide novel molecular insight into how the SC constituents are affected by hydration and heating, and improve the understanding of enhanced SC permeability, which is associated with elevated temperatures and SC hydration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Scheuplein R, Blank IH (1971) Permeability of skin. Physiol Rev 51: 702–747. - PubMed
-
- Weerheim A, Ponec M (2001) Determination of stratum corneum lipid profile by tape stripping in combination with high-performance thin-layer chromatography. Arch Dermatol Res 293: 191–199. - PubMed
-
- Steinert PM, Marekov LN (1995) The proteins elafin, filaggrin, keratin intermediate filaments, loricrin, and small proline-rich protein-1 and protein-2 are isodipeptide cross-linked components of the human epidermal cornified cell-envelope. J Biol Chem 270: 17702–17711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

