Mannose-binding lectin blunts macrophage polarization and ameliorates lupus nephritis
- PMID: 23626823
- PMCID: PMC3633861
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062465
Mannose-binding lectin blunts macrophage polarization and ameliorates lupus nephritis
Abstract
Background: Deficiency in clearance of self nuclear antigens, including DNA, is the hallmark of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), a chronic autoimmnue disease characterized by the production of various autoantibodies, immune complex deposition and severe organ damage. Our previous studies revealed that administration of syngeneic BALB/c mice with activated lymphocyte-derived DNA (ALD-DNA) could induce SLE disease. Mannose-binding lectin (MBL), a secreted pattern recognition receptor with binding activity to DNA, has been proved to be a modulator of inflammation, but whether MBL takes responsibility for DNA clearance, modulates the DNA-mediated immune responses, and is involved in the development of DNA-induced SLE disease remain poorly understood.
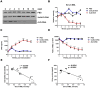
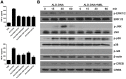
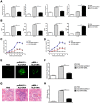
Methodology/principal findings: The levels of serum MBL significantly decreased in lupus mice induced by ALD-DNA and were negatively correlated with SLE disease. MBL blunted macrophage M2b polarization by inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB signaling while enhancing the activation of CREB. Furthermore, MBL suppressed the ability of ALD-DNA-stimulated macrophages to polarize T cells toward Th1 cells and Th17 cells. Importantly, MBL supplement in vivo could ameliorate lupus nephritis.
Conclusion/significance: These results suggest MBL supplement could alleviate SLE disease and might imply a potential therapeutic strategy for DNA-induced SLE, which would further our understanding of the protective role of MBL in SLE disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors (DAI) promotes lupus nephritis by activating the calcium pathway.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 10;288(19):13534-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.457218. Epub 2013 Apr 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23553627 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of macrophage autophagy ameliorates activated lymphocytes-derived DNA induced murine lupus possibly via inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine production.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014 Sep-Oct;32(5):705-14. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25151985
-
Macrophage differentiation and polarization via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-ERK signaling pathway conferred by serum amyloid P component.J Immunol. 2011 Aug 15;187(4):1764-77. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002315. Epub 2011 Jul 13. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21753147
-
Mannose binding lectin (MBL) in autoimmunity and its role in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).J Assoc Physicians India. 2010 Nov;58:688-90. J Assoc Physicians India. 2010. PMID: 21510462 Review.
-
The role of mannose-binding lectin in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Rheumatol. 2008 Apr;27(4):413-9. doi: 10.1007/s10067-008-0838-8. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Clin Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18214570 Review.
Cited by
-
Demethylzeylasteral (T-96) Treatment Ameliorates Mice Lupus Nephritis Accompanied by Inhibiting Activation of NF-κB Pathway.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 24;10(7):e0133724. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133724. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26208003 Free PMC article.
-
Mannan-Binding Lectin Regulates Inflammatory Cytokine Production, Proliferation, and Cytotoxicity of Human Peripheral Natural Killer Cells.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Dec 13;2019:6738286. doi: 10.1155/2019/6738286. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31915415 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of lncRNAs in NF-κB-Mediated Macrophage Inflammation and Their Implications in the Pathogenesis of Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 25;25(5):2670. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052670. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of macrophage polarization by targeted metabolic reprogramming for the treatment of lupus nephritis.Mol Med. 2024 Jun 25;30(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00866-z. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38914953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self DNA from lymphocytes that have undergone activation-induced cell death enhances murine B cell proliferation and antibody production.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 8;9(10):e109095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109095. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25296026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hutcheson J, Scatizzi JC, Siddiqui AM, Haines GK III, Wu T, et al. (2008) Combined deficiency of proapoptotic regulators Bim and Fas results in the early onset of systemic autoimmunity. Immunity 28: 206–217. - PubMed
-
- Nagata S, Hanayama R, Kawane K (2010) Autoimmunity and the Clearance of Dead Cells. Cell 140: 619–630. - PubMed
-
- Munoz LE, Janko C, Schulze C, Schorn C, Sarter K, et al. (2010) Autoimmunity and chronic inflammation - Two clearance-related steps in the etiopathogenesis of SLE. Autoimmunity Reviews 10: 38–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

