Comparative evaluation of short-term biomarker response to treatment for growth hormone deficiency in Chinese children with growth hormone deficiency born small for or appropriate for gestational age: a randomized phase IV open-label study
- PMID: 23626901
- PMCID: PMC3632006
- DOI: 10.1177/2042018813484051
Comparative evaluation of short-term biomarker response to treatment for growth hormone deficiency in Chinese children with growth hormone deficiency born small for or appropriate for gestational age: a randomized phase IV open-label study
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the response between Chinese children with growth hormone deficiency (GHD) born either small for gestational age (SGA) or appropriate for gestational age (AGA) after 4 weeks of recombinant human growth hormone (r-hGH) therapy.
Methods: This was a phase IV, open-label, multicenter, interventional study (NCT01187550). Prepubertal children with GHD received open-label treatment with daily r-hGH (0.033 mg/kg) for 4 weeks. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP3), and metabolic markers (including fasting glucose, insulin, total cholesterol, and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance) were assessed at baseline and after 4 weeks of treatment, and were analyzed according to patient subgroup (SGA or AGA).
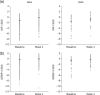
Results: A total of 205 children with GHD (mean age 10.4 years; 175 AGA, 30 SGA) were included in the analysis. Mean baseline serum IGF-I and IGFBP3 standard deviation scores (SDS) across the whole patient population were lower than the population norms (mean values: -2.1 SDS for IGF-I and -1.2 SDS for IGFBP3), with no significant differences between the two patient subgroups. After 4 weeks, IGF-I and IGFBP3 levels increased by 1.0 SDS (p < 0.001) and 0.34 SDS (p < 0.001), respectively, but no significant differences were found between the two patient subgroups for growth-related or metabolic markers.
Conclusions: For children with GHD born SGA, IGF-I and IGFBP3 are short-term biomarkers of responsiveness to treatment with growth hormone, as for children with GHD born AGA.
Keywords: biomarker response; insulin-like growth factor I; insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3; recombinant human growth hormone.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Albertsson-Wikland K. (1989) Growth hormone secretion and growth hormone treatment in children with intrauterine growth retardation. Swedish Paediatric Study Group for Growth Hormone Treatment. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl 349: 35–41 - PubMed
-
- Albertsson-Wikland K., Karlberg J. (1994) Natural growth in children born small for gestational age with and without catch-up growth. Acta Paediatr Suppl 399: 64–70 - PubMed
-
- Bannink E., Djurhuus C., Christensen T., Jøns K., Hokken-Koelega A. (2010) Adult height and health-related quality of life after growth hormone therapy in small for gestational age subjects. J Med Econ 13: 221–227 - PubMed
-
- Boguszewski M., Albertsson-Wikland K., Aronsson S., Gustafsson J., Hagenäs L., Westgren U., et al. (1998) Growth hormone treatment of short children born small-for-gestational-age: the Nordic Multicentre Trial. Acta Paediatr 87: 257–263 - PubMed
-
- Boguszewski M., Jansson C., Rosberg S., Albertsson-Wikland K. (1996) Changes in serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein-3 levels during growth hormone treatment in prepubertal short children born small for gestational age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81: 3902–3908 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

