Serum amyloid A promotes lung neutrophilia by increasing IL-17A levels in the mucosa and γδ T cells
- PMID: 23627303
- PMCID: PMC3778755
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201211-2139OC
Serum amyloid A promotes lung neutrophilia by increasing IL-17A levels in the mucosa and γδ T cells
Abstract
Rationale: Neutrophilic inflammation is an important pathologic feature of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and infectious exacerbations of COPD. Serum amyloid A (SAA) promotes neutrophilic inflammation by its interaction with lung mucosal ALX/FPR2 receptors. However, little is known about how this endogenous mediator regulates IL-17A immunity.
Objectives: To determine whether SAA causes neutrophilic inflammation by IL-17A-dependent mechanisms.
Methods: The relationship between SAA and neutrophils was investigated in lung sections from patients with COPD and a chronic mouse model of SAA exposure. A neutralizing antibody to IL-17A was used to block SAA responses in vivo, and a cell-sorting strategy was used to identify cellular sources.
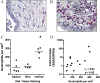
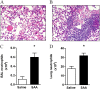
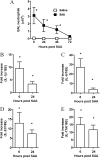
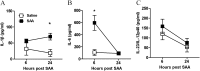
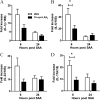
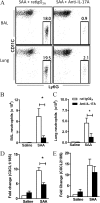
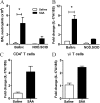
Measurements and main results: SAA mRNA expression was positively associated with tissue neutrophils in COPD (P < 0.05). SAA predominately promoted expression of the TH17 polarizing cytokine IL-6, which was opposed by 15-epi-lipoxin A4, a counter-regulatory mediator, and ALX/FPR2 ligand. SAA-induced inflammation was markedly reduced by a neutralizing antibody to IL-17A in vivo. Cellular sources of IL-17A induced by SAA include CD4(+) T cells, γδ T cells, and an Epcam(+)CD45(-) population enriched for epithelial cells. SAA promotes expression of IL-17A in γδ T cells and this innate cell proportionally expressed higher levels of IL-17A transcript than CD4(+) T cells or epithelial cells.
Conclusions: The SAA-IL-17A axis represents an important innate defense network that may underlie persistent neutrophilic airway inflammation in COPD and modulating the ALX/FPR2 receptor represents a novel approach to targeting aberrant IL-17A-mediated lung immunity.
Figures

References
-
- Hogg JC, Chu F, Utokaparch S, Woods R, Elliott WM, Buzatu L, Cherniack RM, Rogers RM, Sciurba FC, Coxson HO, et al. The nature of small-airway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2645–2653. - PubMed
-
- Culpitt SV, Maziak W, Loukidis S, Nightingale JA, Matthews JL, Barnes PJ. Effect of high dose inhaled steroid on cells, cytokines, and proteases in induced sputum in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:1635–1639. - PubMed
-
- Taggart CC, Greene CM, Carroll TP, O’Neill SJ, McElvaney NG. Elastolytic proteases: inflammation resolution and dysregulation in chronic infective lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171:1070–1076. - PubMed
-
- Papi A, Bellettato CM, Braccioni F, Romagnoli M, Casolari P, Caramori G, Fabbri LM, Johnston SL. Infections and airway inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease severe exacerbations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;173:1114–1121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

