Baculovirus expression: tackling the complexity challenge
- PMID: 23628287
- PMCID: PMC7125881
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.03.009
Baculovirus expression: tackling the complexity challenge
Abstract
Most essential functions in eukaryotic cells are catalyzed by complex molecular machines built of many subunits. To fully understand their biological function in health and disease, it is imperative to study these machines in their entirety. The provision of many essential multiprotein complexes of higher eukaryotes including humans, can be a considerable challenge, as low abundance and heterogeneity often rule out their extraction from native source material. The baculovirus expression vector system (BEVS), specifically tailored for multiprotein complex production, has proven itself to be uniquely suited for overcoming this impeding bottleneck. Here we highlight recent major achievements in multiprotein complex structure research that were catalyzed by this versatile recombinant complex expression tool.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
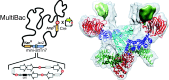


Similar articles
-
Baculovirus expression: old dog, new tricks.Bioengineered. 2015;6(6):316-22. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2015.1104433. Bioengineered. 2015. PMID: 26488462 Free PMC article.
-
The production of multiprotein complexes in insect cells using the baculovirus expression system.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1261:91-114. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2230-7_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25502195
-
MultiBac: Baculovirus-Mediated Multigene DNA Cargo Delivery in Insect and Mammalian Cells.Viruses. 2019 Feb 26;11(3):198. doi: 10.3390/v11030198. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30813511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiprotein complex production in insect cells by using polyproteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1091:131-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-691-7_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24203328 Free PMC article.
-
MultiBac: expanding the research toolbox for multiprotein complexes.Trends Biochem Sci. 2012 Feb;37(2):49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2011.10.005. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012. PMID: 22154230 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protection against Schistosoma mansoni infection using a Fasciola hepatica-derived fatty acid binding protein from different delivery systems.Parasit Vectors. 2016 Apr 18;9:216. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1500-y. Parasit Vectors. 2016. PMID: 27090442 Free PMC article.
-
VLP-factory™ and ADDomer© : Self-assembling Virus-Like Particle (VLP) Technologies for Multiple Protein and Peptide Epitope Display.Curr Protoc. 2021 Mar;1(3):e55. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.55. Curr Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33729713 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Surface and Membrane Engineering: Emerging Technologies and Applications.J Funct Biomater. 2015 Jun 18;6(2):454-85. doi: 10.3390/jfb6020454. J Funct Biomater. 2015. PMID: 26096148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly efficient baculovirus-mediated multigene delivery in primary cells.Nat Commun. 2016 May 4;7:11529. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11529. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27143231 Free PMC article.
-
Expressing of Recombinant VEGFR2-specific Nanobody in Baculovirus Expression System.Iran J Biotechnol. 2021 Jan 1;19(1):e2783. doi: 10.30498/IJB.2021.2783. eCollection 2021 Jan. Iran J Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34179196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bieniossek C., Imasaki T., Takagi Y., Berger I. MultiBac: expanding the research toolbox for multiprotein complexes. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012;37:49–57. - PMC - PubMed
-
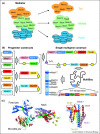
Overview description of the MultiBac BEVS for multiprotein expression, and its applications ranging from structural biology to vaccinology and gene therapy.
-
- Kornberg R.D. Mediator and the mechanism of transcriptional activation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:235. - PubMed
-
- Boube M., Joulia L., Cribbs D.L., Bourbon H.M. Evidence for a mediator of RNA polymerase II transcriptional regulation conserved from yeast to man. Cell. 2002;110:143–151. - PubMed
-
- Kim Y.J., Bjorklund S., Li Y., Sayre M.H., Kornberg R.D. A multiprotein mediator of transcriptional activation and its interaction with the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994;77:599–608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

