Detection of spliced mRNA from human bocavirus 1 in clinical samples from children with respiratory tract infections
- PMID: 23628409
- PMCID: PMC3647721
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1904.121775
Detection of spliced mRNA from human bocavirus 1 in clinical samples from children with respiratory tract infections
Abstract
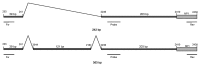
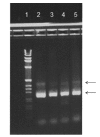
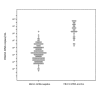
Human bocavirus 1 (HBoV1) is a parvovirus associated with respiratory tract infections (RTIs) in children, but a causal relation has not yet been confirmed. To develop a qualitative reverse transcription PCR to detect spliced mRNA from HBoV1 and to determine whether HBoV1 mRNA correlated better with RTIs than did HBoV1 DNA, we used samples from HBoV1 DNA-positive children, with and without RTIs, to evaluate the test. A real-time reverse transcription PCR, targeting 2 alternatively spliced mRNAs, was developed. HBoV1 mRNA was detected in nasopharyngeal aspirates from 33 (25%) of 133 children with RTIs but in none of 28 controls (p<0.001). The analytical sensitivity and specificity of the test were good. Our data support the hypothesis that HBoV1 may cause RTIs, and we propose that HBoV1 mRNA could be used with benefit, instead of HBoV1 DNA, as a diagnostic target.
Keywords: Human bocavirus; children; mRNA; parvovirus; polymerase chain reaction; respiratory tract infections; splicing; viruses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Diagnosis of Human Bocavirus 1 Respiratory Infection With Messenger RNA Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), DNA Quantitative PCR, and Serology.J Infect Dis. 2017 May 15;215(10):1551-1557. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix169. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28379530
-
Comparison of phenotypic and genotypic diagnosis of acute human bocavirus 1 infection in children.J Clin Virol. 2019 Nov;120:17-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2019.09.003. Epub 2019 Sep 4. J Clin Virol. 2019. PMID: 31521013 Free PMC article.
-
Single detection of human bocavirus 1 with a high viral load in severe respiratory tract infections in previously healthy children.BMC Infect Dis. 2014 Jul 30;14:424. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-14-424. BMC Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25078257 Free PMC article.
-
Human bocaviruses and paediatric infections.Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2019 Jun;3(6):418-426. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(19)30057-4. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2019. PMID: 30948251 Review.
-
Life-Threatening Conditions in Children with Bocavirus Infection-Case Series and Mini Review of the Literature.Viruses. 2024 Aug 23;16(9):1347. doi: 10.3390/v16091347. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39339824 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Viral and Atypical Bacterial Detection in Young Nepalese Children Hospitalized with Severe Pneumonia.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0055121. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00551-21. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34704788 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Quantitative PCR in Evaluating the Clinical Significance of Human Bocavirus Detection in Children.Viruses. 2024 Oct 19;16(10):1637. doi: 10.3390/v16101637. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39459969 Free PMC article.
-
A Diagnostic Approach to Separate Acute Human Bocavirus 1 Respiratory Tract Infection From Long-lasting Virus Shedding.J Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 2;231(5):e862-e866. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaf130. J Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40079329 Free PMC article.
-
Replication of an Autonomous Human Parvovirus in Non-dividing Human Airway Epithelium Is Facilitated through the DNA Damage and Repair Pathways.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Jan 14;12(1):e1005399. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005399. eCollection 2016 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 26765330 Free PMC article.
-
Human Bocavirus 1 Infection of Well-Differentiated Human Airway Epithelium.Curr Protoc Microbiol. 2020 Sep;58(1):e107. doi: 10.1002/cpmc.107. Curr Protoc Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32639683 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonzel L, Tenenbaum T, Schroten H, Schildgen O, Schweitzer-Krantz S, Adams O. Frequent detection of viral coinfection in children hospitalized with acute respiratory tract infection using a real-time polymerase chain reaction. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008;27:589–94 and. 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181694fb9 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
