Adding once-daily lixisenatide for type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by established basal insulin: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled comparison (GetGoal-L)
- PMID: 23628617
- PMCID: PMC3747925
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-2454
Adding once-daily lixisenatide for type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled by established basal insulin: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled comparison (GetGoal-L)
Abstract
Objective: To examine the efficacy and safety of adding the once-daily glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) lixisenatide to established basal insulin therapy alone or together with metformin, in people with type 2 diabetes and elevated glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c).
Research design and methods: We conducted a double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial. Patients (n = 495) with established basal insulin therapy but inadequate glycemic control were randomized to add lixisenatide 20 μg or placebo for 24 weeks. Basal insulin dosage was unchanged except to limit hypoglycemia. HbA1c reduction from baseline was the primary end point.
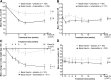
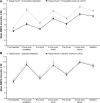
Results: Mean duration of diabetes was 12.5 years, duration of insulin use was 3.1 years, insulin dosage was 55 units/day, and baseline HbA1c was 8.4%. With lixisenatide, the placebo-corrected change of HbA1c from baseline was -0.4% (95% CI -0.6 to -0.2; P = 0.0002), and mean HbA1c at end point was 7.8%. HbA1c <7.0% (53 mmol/mol) was attained by more lixisenatide (28%) than placebo (12%; P < 0.0001) participants. Lixisenatide reduced plasma glucose levels after a standardized breakfast (placebo-corrected reduction, -3.8 mmol/L; P < 0.0001); seven-point glucose profiles showed a reduction persisting through the day. Reductions in body weight (placebo corrected, -1.3 kg; P < 0.0001) and insulin dosage (-3.7 units/day; P = 0.012) were greater with lixisenatide. Main adverse events (AEs) with lixisenatide were gastrointestinal. Symptomatic hypoglycemia was 28% for lixisenatide and 22% for placebo; 4 of 328 subjects (1.2%) had severe hypoglycemia with lixisenatide vs. 0 of 167 with placebo.
Conclusions: By improving HbA1c and postprandial hyperglycemia without weight gain in type 2 diabetes with inadequate glycemic control despite stable basal insulin, lixisenatide may provide an alternative to rapid-acting insulin or other treatment options.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00975286.
Figures
References
-
- IDF Clinical Guidelines Task Force. Global Guideline for Type 2 Diabetes Brussels, International Diabetes Federation, 2005
-
- Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, et al. American Diabetes Association. European Association for the Study of Diabetes Medical management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia 2009;52:17–30 - PubMed
-
- Rodbard HW, Jellinger PS, Davidson JA, et al. Statement by an American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology consensus panel on type 2 diabetes mellitus: an algorithm for glycemic control. Endocr Pract 2009;15:540–559 - PubMed
-
- Riddle MC. Timely initiation of basal insulin. Am J Med 2004;116(Suppl. 3A):3S–9S - PubMed
-
- Riddle MC, Rosenstock J, Gerich J, Insulin Glargine 4002 Study Investigators The treat-to-target trial: randomized addition of glargine or human NPH insulin to oral therapy of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2003;26:3080–3086 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

