Dlic1 deficiency impairs ciliogenesis of photoreceptors by destabilizing dynein
- PMID: 23628724
- PMCID: PMC3674393
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2013.59
Dlic1 deficiency impairs ciliogenesis of photoreceptors by destabilizing dynein
Erratum in
- Cell Res. 2013 Jul;23(7):972. Du, Xinrong [corrected to Du, Xingrong]
Abstract
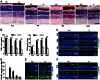
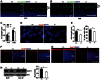
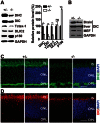
Cytoplasmic dynein 1 is fundamentally important for transporting a variety of essential cargoes along microtubules within eukaryotic cells. However, in mammals, few mutants are available for studying the effects of defects in dynein-controlled processes in the context of the whole organism. Here, we deleted mouse Dlic1 gene encoding DLIC1, a subunit of the dynein complex. Dlic1(-/-) mice are viable, but display severe photoreceptor degeneration. Ablation of Dlic1 results in ectopic accumulation of outer segment (OS) proteins, and impairs OS growth and ciliogenesis of photoreceptors by interfering with Rab11-vesicle trafficking and blocking efficient OS protein transport from Golgi to the basal body. Our studies show that Dlic1 deficiency partially blocks vesicle export from endoplasmic reticulum (ER), but seems not to affect vesicle transport from the ER to Golgi. Further mechanistic study reveals that lack of Dlic1 destabilizes dynein subunits and alters the normal subcellular distribution of dynein in photoreceptors, probably due to the impaired transport function of dynein. Our results demonstrate that Dlic1 plays important roles in ciliogenesis and protein transport to the OS, and is required for photoreceptor development and survival. The Dlic1(-/-) mice also provide a new mouse model to study human retinal degeneration.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Knockout of DLIC1 leads to retinal cone degeneration via disturbing Rab8 transport in zebrafish.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2023 Apr;1869(4):166645. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166645. Epub 2023 Jan 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2023. PMID: 36682603
-
Mutations in the Dynein1 Complex are Permissible for Basal Body Migration in Photoreceptors but Alter Rab6 Localization.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;854:209-15. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-17121-0_28. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26427413 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of a zebrafish dync1h1 mutant reveals multiple functions for cytoplasmic dynein 1 during retinal photoreceptor development.Neural Dev. 2010 Apr 22;5:12. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-5-12. Neural Dev. 2010. PMID: 20412557 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of cytoplasmic dynein on the development and functional maintenance of retinal photoreceptor cells.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Nov;25(21):6539-6547. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202111_27096. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34787856 Review.
-
Review: Cytoplasmic dynein motors in photoreceptors.Mol Vis. 2021 Sep 1;27:506-517. eCollection 2021. Mol Vis. 2021. PMID: 34526758 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assembly and activation of dynein-dynactin by the cargo adaptor protein Hook3.J Cell Biol. 2016 Aug 1;214(3):309-18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201604002. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27482052 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional Deletion of Cytoplasmic Dynein Heavy Chain in Postnatal Photoreceptors.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Nov 1;62(14):23. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.14.23. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 34807236 Free PMC article.
-
Dync1li1 is required for the survival of mammalian cochlear hair cells by regulating the transportation of autophagosomes.PLoS Genet. 2022 Jun 21;18(6):e1010232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010232. eCollection 2022 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 35727824 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of genome-wide knockout mouse database identifies candidate ciliopathy genes.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 1;12(1):20791. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19710-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36456625 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of conditional deletion of cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain DYNC1H1 on postnatal photoreceptors.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 11;16(3):e0248354. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248354. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33705456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tai AW, Chuang JZ, Bode C, Wolfrum U, Sung CH. Rhodopsin's carboxy-terminal cytoplasmic tail acts as a membrane receptor for cytoplasmic dynein by binding to the dynein light chain Tctex-1. Cell. 1999;97:877–887. - PubMed
-
- Wolfrum U, Schmitt A. Rhodopsin transport in the membrane of the connecting cilium of mammalian photoreceptor cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2000;46:95–107. - PubMed
-
- Ramamurthy V, Cayouette M. Development and disease of the photoreceptor cilium. Clin Genet. 2009;76:137–145. - PubMed
-
- Vallee RB, Williams JC, Varma D, Barnhart LE. Dynein: An ancient motor protein involved in multiple modes of transport. J Neurobiol. 2004;58:189–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

