Social ecological predictors of longitudinal HIV treatment adherence in youth with perinatally acquired HIV
- PMID: 23629146
- PMCID: PMC3701127
- DOI: 10.1093/jpepsy/jst017
Social ecological predictors of longitudinal HIV treatment adherence in youth with perinatally acquired HIV
Abstract
Objective: To apply a social ecological model to explore the psychosocial factors prospectively associated with longitudinal adherence to antiretroviral treatment in youth perinatally infected with HIV.
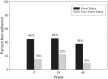
Methods: Randomly selected youth, age 8 to <19 years old, completed cognitive testing and psychosocial questionnaires at baseline as part of a multisite protocol (N = 138). A validated caregiver-report measure of adherence was completed at baseline and 24 and 48 weeks after baseline.
Results: In multivariate analysis, youth awareness of HIV status, caregiver not fully responsible for medications, low caregiver well-being, adolescent perceptions of poor caregiver-youth relations, caregiver perceptions of low social support, and African American ethnicity were associated with nonadherence over 48 weeks.
Conclusions: Interventions focusing on caregivers and their interactions with the individual youth and extrafamilial system should be prioritized for prevention and treatment efforts to address nonadherence during the transition into adolescents.
Keywords: HIV; antiretroviral therapy; children; patient adherence.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson B J, Auslander W F, Jung K C, Miller J P, Santiago J V. Assessing family sharing of diabetes responsibilities. Journal of Pediatric Psychology. 1990;15:477–492. - PubMed
-
- Bronfenbrenner U. The ecology of human development: Experiments by design and nature. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1979.
-
- Drotar D, Levers C. Age differences in parent and child responsibilities for management of cystic fibrosis and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Journal of Development and Behavioral Pediatrics. 1994;15:265–272. - PubMed
-
- Ellis D A, Podolski C L, Frey M, Naar-King S, Wang B, Moltz K. The role of parental monitoring in adolescent health outcomes: Impact on regimen adherence in youth with type 1 diabetes. Journal of Pediatric Psychology. 2007;32:907–917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical