Nuclear corepressors mediate the repression of phospholipase A2 group IIa gene transcription by thyroid hormone
- PMID: 23629656
- PMCID: PMC3675570
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.445569
Nuclear corepressors mediate the repression of phospholipase A2 group IIa gene transcription by thyroid hormone
Abstract
Secretory phospholipase A2 group IIa (PLA2g2a) is associated with inflammation, hyperlipidemia, and atherogenesis. Transcription of the PLA2g2a gene is induced by multiple cytokines. Here, we report the surprising observation that thyroid hormone (T3) inhibited PLA2g2a gene expression in human and rat hepatocytes as well as in rat liver. Moreover, T3 reduced the cytokine-mediated induction of PLA2g2a, suggesting that the thyroid status may modulate aspects of the inflammatory response. In an effort to dissect the mechanism of repression by T3, we cloned the PLA2g2a gene and identified a negative T3 response element in the promoter. This T3 receptor (TRβ)-binding site differed considerably from consensus T3 stimulatory elements. Using in vitro and in vivo binding assays, we found that TRβ bound directly to the PLA2g2a promoter as a heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor. Knockdown of nuclear corepressor or silencing mediator for retinoid and thyroid receptors by siRNA blocked the T3 inhibition of PLA2g2a. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, we showed that nuclear corepressor and silencing mediator for retinoid and thyroid receptors were associated with the PLA2g2a gene in the presence of T3. In contrast with the established role of T3 to promote coactivator association with TRβ, our experiments demonstrate a novel inverse recruitment mechanism in which liganded TRβ recruits corepressors to inhibit PLA2g2a expression.
Keywords: Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase; Corepressor Transcription; Liver; Nuclear Receptors; Phospholipase A; Thyroid Hormone; Thyroid Hormone Receptor; Transcriptional Regulation.
Figures

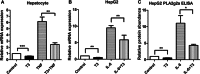

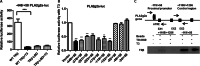






Similar articles
-
Thyroid hormone status regulates the expression of secretory phospholipases.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jan 31;444(1):56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24440706 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory phospholipase A2 group IIA enhances the metabolic rate and increases glucose utilization in response to thyroid hormone.FASEB J. 2019 Jan;33(1):738-749. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800711R. Epub 2018 Jul 18. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30020829
-
Thyroid hormone receptor isoform-specific modification by small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) modulates thyroid hormone-dependent gene regulation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 19;287(43):36499-508. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.344317. Epub 2012 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22930759 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid hormone receptor coactivators and corepressors.Thyroid. 1998 Aug;8(8):703-13. doi: 10.1089/thy.1998.8.703. Thyroid. 1998. PMID: 9737367 Review.
-
Thyroid hormone and thyroid hormone nuclear receptors: History and present state of art.Endocr Regul. 2021 May 21;55(2):103-119. doi: 10.2478/enr-2021-0012. Endocr Regul. 2021. PMID: 34020531 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired Repressor Function in SUMOylation-Defective Thyroid Hormone Receptor Isoforms.Eur Thyroid J. 2016 Sep;5(3):152-163. doi: 10.1159/000447232. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Eur Thyroid J. 2016. PMID: 27843805 Free PMC article.
-
Secretory phospholipase A2 group IIA modulates insulin sensitivity and metabolism.J Lipid Res. 2017 Sep;58(9):1822-1833. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M076141. Epub 2017 Jun 29. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28663239 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted lipidomic analysis and network pharmacology for parthenolide treated papillary thyroid carcinoma cells.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Apr 24;23(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03944-7. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37095470 Free PMC article.
-
Stalling of the endometrial decidual reaction determines the recurrence risk of miscarriage.Sci Adv. 2025 Jun 27;11(26):eadv1988. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adv1988. Epub 2025 Jun 25. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40561039 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric pathways in nuclear receptors - Potential targets for drug design.Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Mar;183:152-159. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.10.014. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29080700 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lambeau G., Gelb M. H. (2008) Biochemistry and physiology of mammalian secreted phospholipases A2. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 77, 495–520 - PubMed
-
- Murakami M., Taketomi Y., Girard C., Yamamoto K., Lambeau G. (2010) Emerging roles of secreted phospholipase A2 enzymes. Lessons from transgenic and knockout mice. Biochimie 92, 561–582 - PubMed
-
- Arsenault B. J., Boekholdt S. M., Kastelein J. J. (2011) Varespladib. Targeting the inflammatory face of atherosclerosis. Eur. Heart J. 32, 923–926 - PubMed
-
- Leitinger N., Watson A. D., Hama S. Y., Ivandic B., Qiao J. H., Huber J., Faull K. F., Grass D. S., Navab M., Fogelman A. M., de Beer F. C., Lusis A. J., Berliner J. A. (1999) Role of group II secretory phospholipase A2 in atherosclerosis. 2. Potential involvement of biologically active oxidized phospholipids. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 19, 1291–1298 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

