Insights into the photoprotective switch of the major light-harvesting complex II (LHCII): a preserved core of arginine-glutamate interlocked helices complemented by adjustable loops
- PMID: 23629658
- PMCID: PMC3707683
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.456111
Insights into the photoprotective switch of the major light-harvesting complex II (LHCII): a preserved core of arginine-glutamate interlocked helices complemented by adjustable loops
Abstract
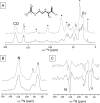
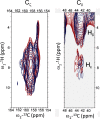
Light-harvesting antennae of the LHC family form transmembrane three-helix bundles of which two helices are interlocked by conserved arginine-glutamate (Arg-Glu) ion pairs that form ligation sites for chlorophylls. The antenna proteins of photosystem II have an intriguing dual function. In excess light, they can switch their conformation from a light-harvesting into a photoprotective state, in which the excess and harmful excitation energies are safely dissipated as heat. Here we applied magic angle spinning NMR and selective Arg isotope enrichment as a noninvasive method to analyze the Arg structures of the major light-harvesting complex II (LHCII). The conformations of the Arg residues that interlock helix A and B appear to be preserved in the light-harvesting and photoprotective state. Several Arg residues have very downfield-shifted proton NMR responses, indicating that they stabilize the complex by strong hydrogen bonds. For the Arg Cα chemical shifts, differences are observed between LHCII in the active, light-harvesting and in the photoprotective, quenched state. These differences are attributed to a conformational change of the Arg residue in the stromal loop region. We conclude that the interlocked helices of LHCII form a rigid core. Consequently, the LHCII conformational switch does not involve changes in A/B helix tilting but likely involves rearrangements of the loops and helical segments close to the stromal and lumenal ends.
Keywords: Bioenergetics; LHC Family; Non-photochemical Quenching; Photosynthesis; Photosynthetic Light Harvesting; Photosystem II; Protein Conformation; Solid-state NMR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modeling the NMR signatures associated with the functional conformational switch in the major light-harvesting antenna of photosystem II in higher plants.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2014 Mar 28;16(12):5571-80. doi: 10.1039/c3cp54971b. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2014. PMID: 24513782
-
An NMR comparison of the light-harvesting complex II (LHCII) in active and photoprotective states reveals subtle changes in the chlorophyll a ground-state electronic structures.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jun;1827(6):738-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.02.015. Epub 2013 Mar 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23466337
-
First solid-state NMR analysis of uniformly ¹³C-enriched major light-harvesting complexes from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and identification of protein and cofactor spin clusters.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Apr;1807(4):437-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.01.007. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21276419
-
A perspective on the major light-harvesting complex dynamics under the effect of pH, salts, and the photoprotective PsbS protein.Photosynth Res. 2023 Apr;156(1):163-177. doi: 10.1007/s11120-022-00935-6. Epub 2022 Jul 10. Photosynth Res. 2023. PMID: 35816266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions and Evolution of Lhcb Isoforms Composing LHCII, the Major Light Harvesting Complex of Photosystem II of Green Eukaryotic Organisms.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018;19(7):699-713. doi: 10.2174/1389203719666180222101534. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2018. PMID: 29473498 Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering the interactions driving carotenoid binding in light-harvesting complexes.Chem Sci. 2021 Feb 15;12(14):5113-5122. doi: 10.1039/d1sc00071c. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34163750 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic labeling with stable isotope nitrogen (15N) to follow amino acid and protein turnover of three plastid proteins in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Proteome Sci. 2014 Mar 3;12(1):14. doi: 10.1186/1477-5956-12-14. Proteome Sci. 2014. PMID: 24580857 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational Dynamics of Light-Harvesting Complex II in a Native Membrane Environment.Biophys J. 2021 Jan 19;120(2):270-283. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.11.2265. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 33285116 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of the N-terminal Section and the Lumenal Loop of Trimeric Light Harvesting Complex II (LHCII) by Using EPR.J Biol Chem. 2015 Oct 23;290(43):26007-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.669804. Epub 2015 Aug 27. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26316535 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular dynamics simulations in photosynthesis.Photosynth Res. 2020 May;144(2):273-295. doi: 10.1007/s11120-020-00741-y. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Photosynth Res. 2020. PMID: 32297102 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ballottari M., Girardon J., Dall'osto L., Bassi R. (2012) Evolution and functional properties of photosystem II light harvesting complexes in eukaryotes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1817, 143–157 - PubMed
-
- Liu Z., Yan H., Wang K., Kuang T., Zhang J., Gui L., An X., Chang W. (2004) Crystal structure of spinach major light-harvesting complex at 2.72 Ä resolution. Nature 428, 287–292 - PubMed
-
- Barros T., Kühlbrandt W. (2009) Crystallisation, structure, and function of plant light-harvesting Complex II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1787, 753–772 - PubMed
-
- Ruban A. V., Johnson M. P., Duffy C. D. P. (2012) The photoprotective molecular switch in the photosystem II antenna. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1817, 167–181 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

