Insights into the photoprotective switch of the major light-harvesting complex II (LHCII): a preserved core of arginine-glutamate interlocked helices complemented by adjustable loops
- PMID: 23629658
- PMCID: PMC3707683
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.456111
Insights into the photoprotective switch of the major light-harvesting complex II (LHCII): a preserved core of arginine-glutamate interlocked helices complemented by adjustable loops
Abstract
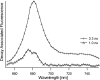
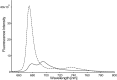
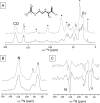
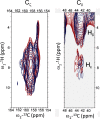
Light-harvesting antennae of the LHC family form transmembrane three-helix bundles of which two helices are interlocked by conserved arginine-glutamate (Arg-Glu) ion pairs that form ligation sites for chlorophylls. The antenna proteins of photosystem II have an intriguing dual function. In excess light, they can switch their conformation from a light-harvesting into a photoprotective state, in which the excess and harmful excitation energies are safely dissipated as heat. Here we applied magic angle spinning NMR and selective Arg isotope enrichment as a noninvasive method to analyze the Arg structures of the major light-harvesting complex II (LHCII). The conformations of the Arg residues that interlock helix A and B appear to be preserved in the light-harvesting and photoprotective state. Several Arg residues have very downfield-shifted proton NMR responses, indicating that they stabilize the complex by strong hydrogen bonds. For the Arg Cα chemical shifts, differences are observed between LHCII in the active, light-harvesting and in the photoprotective, quenched state. These differences are attributed to a conformational change of the Arg residue in the stromal loop region. We conclude that the interlocked helices of LHCII form a rigid core. Consequently, the LHCII conformational switch does not involve changes in A/B helix tilting but likely involves rearrangements of the loops and helical segments close to the stromal and lumenal ends.
Keywords: Bioenergetics; LHC Family; Non-photochemical Quenching; Photosynthesis; Photosynthetic Light Harvesting; Photosystem II; Protein Conformation; Solid-state NMR.
Figures


References
-
- Ballottari M., Girardon J., Dall'osto L., Bassi R. (2012) Evolution and functional properties of photosystem II light harvesting complexes in eukaryotes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1817, 143–157 - PubMed
-
- Liu Z., Yan H., Wang K., Kuang T., Zhang J., Gui L., An X., Chang W. (2004) Crystal structure of spinach major light-harvesting complex at 2.72 Ä resolution. Nature 428, 287–292 - PubMed
-
- Barros T., Kühlbrandt W. (2009) Crystallisation, structure, and function of plant light-harvesting Complex II. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1787, 753–772 - PubMed
-
- Ruban A. V., Johnson M. P., Duffy C. D. P. (2012) The photoprotective molecular switch in the photosystem II antenna. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1817, 167–181 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

