Oxidative stress mediates the disruption of airway epithelial tight junctions through a TRPM2-PLCγ1-PKCα signaling pathway
- PMID: 23629676
- PMCID: PMC3676794
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms14059475
Oxidative stress mediates the disruption of airway epithelial tight junctions through a TRPM2-PLCγ1-PKCα signaling pathway
Abstract
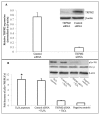
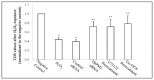
Oxidative stress has been implicated as an important contributing factor in the pathogenesis of several pulmonary inflammatory diseases. Previous studies have indicated a relationship between oxidative stress and the attenuation of epithelial tight junctions (TJs). In Human Bronchial Epithelial-16 cells (16HBE), we demonstrated the degradation of zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), and claudin-2 exhibited a great dependence on the activation of the transient receptor potential melastatin (TRPM) 2 channel, phospholipase Cγ1 (PLCγ1) and the protein kinase Cα (PKCα) signaling cascade.
Figures


References
-
- Tomita K., Barnes P.J., Adcock I.M. The effect of oxidative stress on histone acetylation and IL-8 release. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003;301:572–577. - PubMed
-
- Van Itallie C.M., Anderson J.M. The molecular physiology of tight junction pores. Physiology. 2004;19:331–338. - PubMed
-
- Balda M.S., Matter K. Tight junctions and the regulation of gene expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009;1788:761–767. - PubMed
-
- Wang F., Daugherty B., Keise L.L., Wei Z., Foley J.P., Savani R.C., Koval M. Heterogeneity of claudin expression by alveolar epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2003;29:62–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

