The Staphylococcus aureus thiol/oxidative stress global regulator Spx controls trfA, a gene implicated in cell wall antibiotic resistance
- PMID: 23629700
- PMCID: PMC3697328
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00220-13
The Staphylococcus aureus thiol/oxidative stress global regulator Spx controls trfA, a gene implicated in cell wall antibiotic resistance
Abstract
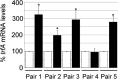
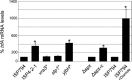
S. aureus combats cell wall antibiotic stress by altered gene expression mediated by various environmental signal sensors. In this study, we examined the transcriptional regulation of trfA, a gene related to mecA of Bacillus subtilis encoding an adaptor protein implicated in multiple roles, notably, proteolysis and genetic competence. Despite strong sequence similarity to B. subtilis mecA, the function of S. aureus trfA remains largely unexplored; however, its deletion leads to almost complete loss of resistance to oxacillin and glycopeptide antibiotics in glycopeptide-intermediate S. aureus (GISA) derivatives of methicillin-susceptible or methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) clinical or laboratory isolates. Northern blot analysis and 5' rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) mapping revealed that trfA was expressed monocistronically by three promoters. Cell wall-active antibiotic exposure led to both increased trfA transcription and enhanced steady-state TrfA levels. trfA promoter regulation was not dependent upon the cell wall stress sentinel VraSR and other sensory stress systems, such as GraRS, WalkRK, Stk1/Stp1, and SigB. Notably, we discovered that the global oxidative-stress regulator Spx controlled trfA transcription. This finding was also confirmed using a strain with enhanced Spx levels resulting from a defect in yjbH, encoding a Spx-interacting protein governing Spx proteolytic degradation. A cohort of clinical GISA strains revealed significant steady-state upregulation of trfA compared to corresponding susceptible parental strains, further supporting a role for trfA in antibiotic resistance. These data provide strong evidence for a link between cell wall antibiotic stress and evoked responses mediated by an oxidative-stress sensor.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Role of adaptor TrfA and ClpPC in controlling levels of SsrA-tagged proteins and antitoxins in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2014 Dec;196(23):4140-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.02222-14. Epub 2014 Sep 15. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 25225270 Free PMC article.
-
Two-component system VraSR positively modulates the regulation of cell-wall biosynthesis pathway in Staphylococcus aureus.Mol Microbiol. 2003 Aug;49(3):807-21. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03599.x. Mol Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12864861
-
Rifampin Resistance rpoB Alleles or Multicopy Thioredoxin/Thioredoxin Reductase Suppresses the Lethality of Disruption of the Global Stress Regulator spx in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2016 Sep 9;198(19):2719-31. doi: 10.1128/JB.00261-16. Print 2016 Oct 1. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 27432833 Free PMC article.
-
Driving Forces of Mechanisms Regulating Oxacillin-Resistance Phenotypes of MRSA: Truly Oxacillin-Susceptible mecA-Positive Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates also Exist.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(16):2048-53. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150310103754. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 25760336 Review.
-
Direction of aminoacylated transfer RNAs into antibiotic synthesis and peptidoglycan-mediated antibiotic resistance.FEBS Lett. 2013 Sep 17;587(18):2895-904. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Jul 29. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23907010 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Transcription of Oxidative Stress Genes Is Directly Activated by SpxA1 and, to a Lesser Extent, by SpxA2 in Streptococcus mutans.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jul;197(13):2160-2170. doi: 10.1128/JB.00118-15. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25897032 Free PMC article.
-
Two Spx regulators modulate stress tolerance and virulence in Streptococcus suis serotype 2.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 29;9(9):e108197. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108197. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25264876 Free PMC article.
-
MazF toxin causes alterations in Staphylococcus aureus transcriptome, translatome and proteome that underlie bacterial dormancy.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Feb 26;49(4):2085-2101. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa1292. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33544858 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Achilles' Heel of Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus by the Endocannabinoid Anandamide.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 14;23(14):7798. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147798. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887146 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory circuits controlling Spx levels in Streptococcus mutans.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Jul;114(1):109-126. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14499. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32189382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lowy FD. 1998. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 339:520–532 - PubMed
-
- Howden BP, Davies JK, Johnson PD, Stinear TP, Grayson ML. 2010. Reduced vancomycin susceptibility in Staphylococcus aureus, including vancomycin-intermediate and heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate strains: resistance mechanisms, laboratory detection, and clinical implications. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 23:99–139 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gould IM, Cauda R, Esposito S, Gudiol F, Mazzei T, Garau J. 2011. Management of serious meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: what are the limits? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 37:202–209 - PubMed
-
- Kullar R, Davis SL, Levine DP, Rybak MJ. 2011. Impact of vancomycin exposure on outcomes in patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: support for consensus guidelines suggested targets. Clin. Infect. Dis. 52:975–981 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

