Stress granules as crucibles of ALS pathogenesis
- PMID: 23629963
- PMCID: PMC3639398
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201302044
Stress granules as crucibles of ALS pathogenesis
Abstract
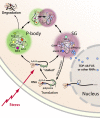
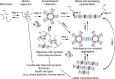
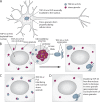
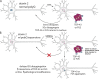
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a fatal human neurodegenerative disease affecting primarily motor neurons. Two RNA-binding proteins, TDP-43 and FUS, aggregate in the degenerating motor neurons of ALS patients, and mutations in the genes encoding these proteins cause some forms of ALS. TDP-43 and FUS and several related RNA-binding proteins harbor aggregation-promoting prion-like domains that allow them to rapidly self-associate. This property is critical for the formation and dynamics of cellular ribonucleoprotein granules, the crucibles of RNA metabolism and homeostasis. Recent work connecting TDP-43 and FUS to stress granules has suggested how this cellular pathway, which involves protein aggregation as part of its normal function, might be coopted during disease pathogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Arai T., Hasegawa M., Akiyama H., Ikeda K., Nonaka T., Mori H., Mann D., Tsuchiya K., Yoshida M., Hashizume Y., Oda T. 2006. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351:602–611 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.093 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01NS073660/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 OD004417/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R21HD074510/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM099836/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD074510/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM099836/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS073660/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS067354/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- DP2OD004417/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 OD002177/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- DP2OD002177/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS065317/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065317/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS067354/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

