Arginine-based cationic liposomes for efficient in vitro plasmid DNA delivery with low cytotoxicity
- PMID: 23630419
- PMCID: PMC3626367
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S38903
Arginine-based cationic liposomes for efficient in vitro plasmid DNA delivery with low cytotoxicity
Abstract
Background: Currently available gene delivery vehicles have many limitations such as low gene delivery efficiency and high cytotoxicity. To overcome these drawbacks, we designed and synthesized two cationic lipids comprised of n-tetradecyl alcohol as the hydrophobic moiety, 3-hydrocarbon chain as the spacer, and different counterions (eg, hydrogen chloride [HCl] salt or trifluoroacetic acid [TFA] salt) in the arginine head group.
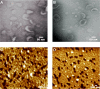
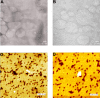
Methods: Cationic lipids were hydrated in 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) buffer to prepare cationic liposomes and characterized in terms of their size, zeta potential, phase transition temperature, and morphology. Lipoplexes were then prepared and characterized in terms of their size and zeta potential in the absence or presence of serum. The morphology of the lipoplexes was determined using transmission electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy. The gene delivery efficiency was evaluated in neuronal cells and HeLa cells and compared with that of lysine-based cationic assemblies and Lipofectamine™ 2000. The cytotoxicity level of the cationic lipids was investigated and compared with that of Lipofectamine™ 2000.
Results: We synthesized arginine-based cationic lipids having different counterions (ie, HCl-salt or TFA-salt) that formed cationic liposomes of around 100 nm in size. In the absence of serum, lipoplexes prepared from the arginine-based cationic liposomes and plasmid (p) DNA formed large aggregates and attained a positive zeta potential. However, in the presence of serum, the lipoplexes were smaller in size and negative in zeta potential. The morphology of the lipoplexes was vesicular. Arginine-based cationic liposomes with HCl-salt showed the highest transfection efficiency in PC-12 cells. However, arginine-based cationic liposomes with TFA salt showed the highest transfection efficiency in HeLa cells, regardless of the presence of serum, with very low associated cytotoxicity.
Conclusion: The gene delivery efficiency of amino acid-based cationic assemblies is influenced by the amino acids (ie, arginine or lysine) present as the hydrophilic head group and their associated counterions.
Keywords: cationic liposome; counterions; cytotoxicity; pDNA; transfection efficiency.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson WF. Human gene therapy. Nature. 1998;392(Suppl 6679):25–30. - PubMed
-
- Corso TD, Torres G, Goulah C, et al. Transfection of tyrosine kinase deleted FGF receptor-1 into rat brain substantia nigra reduces the number of tyrosine hydroxylase expressing neurons and decreases concentration levels of striatal dopamine. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005;139(2):361–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

