Imaging zebrafish neural circuitry from whole brain to synapse
- PMID: 23630470
- PMCID: PMC3634052
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00076
Imaging zebrafish neural circuitry from whole brain to synapse
Abstract
Recent advances in imaging tools are inspiring zebrafish researchers to tackle ever more ambitious questions in the neurosciences. Behaviorally fundamental conserved neural networks can now be potentially studied using zebrafish from a brain-wide scale to molecular resolution. In this perspective, we offer a roadmap by which a zebrafish researcher can navigate the course from collecting neural activities across the brain associated with a behavior, to unraveling molecular identities and testing the functional relevance of active neurons. In doing so, important insights will be gained as to how neural networks generate behaviors and assimilate changes in synaptic connectivity.
Keywords: array tomography; calcium imaging; clinical neuroscience; psychiatry; synapse imaging; whole brain imaging; zebrafish.
Figures
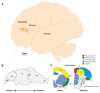
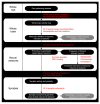
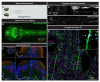
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

