Metabolic changes one year after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding operation in morbidly obese subjects
- PMID: 23630549
- PMCID: PMC3627148
- DOI: 10.5114/wiitm.2011.30828
Metabolic changes one year after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding operation in morbidly obese subjects
Abstract
Introduction: Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) is effective for weight reduction in severely obese patients. However, the data about its effect on metabolic syndrome (MS) are limited.
Aim: To assess weight loss and changes of metabolic parameters 1 year after LAGB in a prospective, nonrandomized single center cohort study in morbidly obese subjects.
Material and methods: Physical examination, body weight (BW) parameters and metabolic profile were assessed at baseline and 1 year after LAGB in morbidly obese subjects. The incidence of MS was evaluated according to National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III criteria.
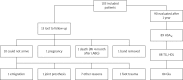
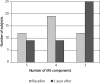
Results: One year after the operation data from 90 patients out of 103 were available. Mean excess weight (EW) loss of 33.1% was associated with a significant improvement in all metabolic parameters: decrease of hypertension by 15.8%, hypertriglyceridemia by 42.6%, and hyperglycemia by 46.3%; and increase in high density lipoprotein cholesterol by 48.3%. This resulted in the resolution of MS in 44.2% of subjects. The significant change in the distribution of MS components was observed with the highest frequency of 4 components before and 2 components after surgery. Patients with MS at baseline lost 29.9% of EW compared to 44.3% in those without MS (p = 0.009).
Conclusions: The LAGB resulted in effective reduction of BW parameters in morbidly obese subjects 1 year after the operation. Along with the weight loss, resolution of MS and a significant shift towards decrease in the number of MS components was observed. Patients with MS were more resistant to the weight loss.
Keywords: bariatric surgery; laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding; metabolic syndrome; obesity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding on metabolic syndrome and its risk factors in morbidly obese adolescents.J Obes. 2011;2011:906384. doi: 10.1155/2011/906384. Epub 2010 Nov 7. J Obes. 2011. PMID: 21188168 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding for morbidly obese adolescents affects android fat loss, resolution of comorbidities, and improved metabolic status.J Am Coll Surg. 2009 Nov;209(5):638-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2009.07.022. Epub 2009 Aug 29. J Am Coll Surg. 2009. PMID: 19854406
-
Weight loss and metabolic improvements in obese patients undergoing gastric banding and gastric banded plication: A comparison.Nutrition. 2019 Jan;57:290-299. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.05.024. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Nutrition. 2019. PMID: 30219686
-
Bariatric surgery for the treatment of morbid obesity: a meta-analysis of weight loss outcomes for laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and laparoscopic gastric bypass.Obes Surg. 2009 Oct;19(10):1447-55. doi: 10.1007/s11695-009-9927-2. Epub 2009 Aug 5. Obes Surg. 2009. PMID: 19655209 Review.
-
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: which has a place in the treatment of diabetes in morbidly obese patients?Diabetes Metab. 2009 Dec;35(6 Pt 2):524-7. doi: 10.1016/S1262-3636(09)73460-3. Diabetes Metab. 2009. PMID: 20152738 Review.
Cited by
-
Bariatric Surgery and Remission of Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials and Prospective Studies.Obes Surg. 2025 Apr;35(4):1337-1349. doi: 10.1007/s11695-025-07750-7. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Obes Surg. 2025. PMID: 40000567
-
Discovery of novel potential 11β-HSD1 inhibitors through combining deep learning, molecular modeling, and bio-evaluation.Mol Divers. 2025 Aug;29(4):3485-3500. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11171-0. Epub 2025 May 21. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 40397334
-
An evaluation of the knowledge of the surgical treatment of obesity among surgeons.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2014 Mar;9(1):6-12. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2014.40160. Epub 2014 Jan 25. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2014. PMID: 24729803 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of type 2 diabetes mellitus laboratory remission after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in patients with body mass index lower than 35 kg/m(2) and higher than 35 kg/m(2) in a 3-year observation period.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2014 Dec;9(4):523-30. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2014.44427. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2014. PMID: 25561989 Free PMC article.
-
Does the length of the biliary limb influence medium-term laboratory remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in morbidly obese patients?Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2014 Mar;9(1):31-9. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2014.40383. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2014. PMID: 24729807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dixon JB, Murphy DK, Segel JE, et al. Impact of laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding on type 2 diabetes. Obes Rev. 2012;13:57–67. - PubMed
-
- Gasteyger C, Suter M, Calmes JM, et al. Changes in body composition, metabolic profile and nutritional status 24 months after gastric banding. Obes Surg. 2006;16:243–50. - PubMed
-
- Lee WJ, Huang MT, Wang W, et al. Effects of obesity surgery on the metabolic syndrome. Arch Surg. 2004;139:1088–92. - PubMed
-
- Kwiatkowski A, Paśnik K, Stanowski E, Badyda A. Regression of metabolic syndrome depending on type of bariatric surgery. Videosurgery Miniinv. 2009;4:53–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
