Targeted deletion of the ERK5 MAP kinase impairs neuronal differentiation, migration, and survival during adult neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb
- PMID: 23630619
- PMCID: PMC3632513
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061948
Targeted deletion of the ERK5 MAP kinase impairs neuronal differentiation, migration, and survival during adult neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb
Abstract
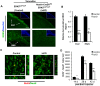
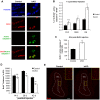
Recent studies have led to the exciting idea that adult-born neurons in the olfactory bulb (OB) may be critical for complex forms of olfactory behavior in mice. However, signaling mechanisms regulating adult OB neurogenesis are not well defined. We recently reported that extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 5, a MAP kinase, is specifically expressed in neurogenic regions within the adult brain. This pattern of expression suggests a role for ERK5 in the regulation of adult OB neurogenesis. Indeed, we previously reported that conditional deletion of erk5 in adult neurogenic regions impairs several forms of olfactory behavior in mice. Thus, it is important to understand how ERK5 regulates adult neurogenesis in the OB. Here we present evidence that shRNA suppression of ERK5 in adult neural stem/progenitor cells isolated from the subventricular zone (SVZ) reduces neurogenesis in culture. By contrast, ectopic activation of endogenous ERK5 signaling via expression of constitutive active MEK5, an upstream activating kinase for ERK5, stimulates neurogenesis. Furthermore, inducible and conditional deletion of erk5 specifically in the neurogenic regions of the adult mouse brain interferes with cell cycle exit of neuroblasts, impairs chain migration along the rostral migratory stream and radial migration into the OB. It also inhibits neuronal differentiation and survival. These data suggest that ERK5 regulates multiple aspects of adult OB neurogenesis and provide new insights concerning signaling mechanisms governing adult neurogenesis in the SVZ-OB axis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures








Similar articles
-
Inducible activation of ERK5 MAP kinase enhances adult neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb and improves olfactory function.J Neurosci. 2015 May 20;35(20):7833-49. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3745-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25995470 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible and conditional deletion of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 disrupts adult hippocampal neurogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 6;287(28):23306-17. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.344762. Epub 2012 May 29. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22645146 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible and targeted deletion of the ERK5 MAP kinase in adult neurogenic regions impairs adult neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb and several forms of olfactory behavior.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49622. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049622. Epub 2012 Nov 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23185386 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory bulb neurogenesis depending on signaling in the subventricular zone.Cereb Cortex. 2023 Nov 4;33(22):11102-11111. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhad349. Cereb Cortex. 2023. PMID: 37746807 Review.
-
Relationship between Blood Vessels and Migration of Neuroblasts in the Olfactory Neurogenic Region of the Rodent Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 25;22(21):11506. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111506. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768936 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inducible and conditional activation of ERK5 MAP kinase rescues mice from cadmium-induced olfactory memory deficits.Neurotoxicology. 2020 Dec;81:127-136. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2020.09.038. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Neurotoxicology. 2020. PMID: 33039505 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 5 is Required for Low-Concentration H2O2-Induced Angiogenesis of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells.Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:6895730. doi: 10.1155/2017/6895730. Epub 2017 Apr 30. Biomed Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28540300 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of irradiating the subventricular zone stem cell niche.Stem Cell Res. 2016 Mar;16(2):387-96. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2016.02.031. Epub 2016 Feb 17. Stem Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 26921873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A hydroxylated metabolite of flame-retardant PBDE-47 decreases the survival, proliferation, and neuronal differentiation of primary cultured adult neural stem cells and interferes with signaling of ERK5 MAP kinase and neurotrophin 3.Toxicol Sci. 2013 Jul;134(1):111-24. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft083. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Toxicol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23564643 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of Cav1.3 channels in dorsal hippocampus impairs the development of dentate gyrus newborn neurons and hippocampal-dependent memory tasks.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 17;12(7):e0181138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181138. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28715454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman J (1969) Autoradiographic and histological studies of postnatal neurogenesis. IV. Cell proliferation and migration in the anterior forebrain, with special reference to persisting neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 137: 433–457. - PubMed
-
- Doetsch F, Caille I, Lim DA, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A (1999) Subventricular zone astrocytes are neural stem cells in the adult mammalian brain. Cell 97: 703–716. - PubMed
-
- Gage FH (2000) Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 287: 1433–1438. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

