Transcriptome analysis of crucian carp (Carassius auratus), an important aquaculture and hypoxia-tolerant species
- PMID: 23630630
- PMCID: PMC3632525
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062308
Transcriptome analysis of crucian carp (Carassius auratus), an important aquaculture and hypoxia-tolerant species
Abstract
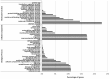
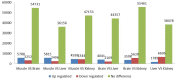
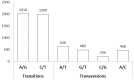
The crucian carp is an important aquaculture species and a potential model to study genome evolution and physiological adaptation. However, so far the genomics and transcriptomics data available for this species are still scarce. We performed de novo transcriptome sequencing of four cDNA libraries representing brain, muscle, liver and kidney tissues respectively, each with six specimens. The removal of low quality reads resulted in 2.62 million raw reads, which were assembled as 127,711 unigenes, including 84,867 isotigs and 42,844 singletons. A total of 22,273 unigenes were found with significant matches to 14,449 unique proteins. Around14,398 unigenes were assigned with at least one Gene Ontology (GO) category in 84,876 total assignments, and 6,382 unigenes were found in 237 predicted KEGG pathways. The gene expression analysis revealed more genes expressed in brain, more up-regulated genes in muscle and more down-regulated genes in liver as compared with gene expression profiles of other tissues. In addition, 23 enzymes in the glycolysis/gluconeogenesis pathway were recovered. Importantly, we identified 5,784 high-quality putative SNP and 11,295 microsatellite markers which include 5,364 microsatellites with flanking sequences ≥50 bp. This study produced the most comprehensive genomic resources that have been derived from crucian carp, including thousands of genetic markers, which will not only lay a foundation for further studies on polyploidy origin and anoxic survival but will also facilitate selective breeding of this important aquaculture species.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic Profiles of Brain Provide Insights into Molecular Mechanism of Feed Conversion Efficiency in Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus).Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 14;19(3):858. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030858. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29538345 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly and characterization of the spleen transcriptome of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) using Illumina paired-end sequencing.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 Jun;44(2):420-9. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25804493
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals hypoxic response key genes and modules as well as adaptive mechanism of crucian carp (Carassius auratus) gill under hypoxic stress.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 5;16:1543605. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1543605. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39975546 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling of developing spleen tissue and discovery of immune-related genes in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017 Jan;60:400-410. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.12.012. Epub 2016 Dec 11. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27965162
-
Role of Phytobiotics in Modulating Transcriptomic Profile in Carps: A Mini-Review.Biochem Genet. 2024 Oct;62(5):3285-3304. doi: 10.1007/s10528-023-10606-3. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Biochem Genet. 2024. PMID: 38167984 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-seq and qRT-PCR analyses reveal the physiological response to acute hypoxia and reoxygenation in Epinephelus coioides.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 3;13:1049776. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1049776. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36406980 Free PMC article.
-
The transcriptomic responses of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) to acute hypoxia stress alone, and in combination with bortezomib.BMC Genomics. 2022 Feb 25;23(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08399-7. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35216548 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of flower-bud transcriptome and development of genic SSR markers in Asian lotus (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.).PLoS One. 2014 Nov 7;9(11):e112223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112223. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25379700 Free PMC article.
-
De novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of male, pseudo-male and female yellow perch, Perca flavescens.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 3;12(2):e0171187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171187. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28158238 Free PMC article.
-
De novo transcriptome based on next-generation sequencing reveals candidate genes with sex-specific expression in Arapaima gigas (Schinz, 1822), an ancient Amazonian freshwater fish.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 29;13(10):e0206379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206379. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30372461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen XL, Huang HJ (1982) Cyprininae. In: Wu, X.W. (eds) Monographs of Cyprinidae in China, Shanghai People’s Press, Shanghai.
-
- FAO website. Available: http://www.fao.org/fishery/culturedspecies/Carassius_carassius/en. Accessed 2012 Jul 23.
-
- Wang J, Qin Q, Chen S (2008) Formation and biological characterization of three new types of improved crucian carp. Sci China C Life Sci 51: 544–551. - PubMed
-
- Gui JF, Zhou L (2010) Genetic basis and breeding application of clonal diversity and dual reproduction modes in polyploid Carassius auratus gibelio . Sci China C Life Sci 53: 409–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

