Neonatal disruption of serine racemase causes schizophrenia-like behavioral abnormalities in adulthood: clinical rescue by d-serine
- PMID: 23630632
- PMCID: PMC3632541
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062438
Neonatal disruption of serine racemase causes schizophrenia-like behavioral abnormalities in adulthood: clinical rescue by d-serine
Abstract
Background: D-Serine, an endogenous co-agonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, is synthesized from L-serine by serine racemase (SRR). Given the role of D-serine in both neurodevelopment and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia, we examined whether neonatal disruption of D-serine synthesis by SRR inhibition could induce behavioral abnormalities relevant to schizophrenia, in later life.
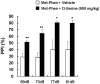
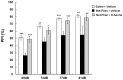
Methodology/principal findings: Neonatal mice (7-9 days) were injected with vehicle or phenazine methosulfate (Met-Phen: 3 mg/kg/day), an SRR inhibitor. Behavioral evaluations, such as spontaneous locomotion, novel object recognition test (NORT), and prepulse inhibition (PPI) were performed at juvenile (5-6 weeks old) and adult (10-12 weeks old) stages. In addition, we tested the effects of D-serine on PPI deficits in adult mice after neonatal Met-Phen exposure. Finally, we assessed whether D-serine could prevent the onset of schizophrenia-like behavior in these mice. Neonatal Met-Phen treatment reduced D-serine levels in the brain, 24 hours after the final dose. Additionally, this treatment caused behavioral abnormalities relevant to prodromal symptoms in juveniles and to schizophrenia in adults. A single dose of D-serine improved PPI deficits in adult mice. Interestingly, chronic administration of D-serine (900 mg/kg/day from P35 to P70) significantly prevented the onset of PPI deficits after neonatal Met-Phen exposure.
Conclusions/significance: This study shows that disruption of D-serine synthesis during developmental stages leads to behavioral abnormalities relevant to prodromal symptoms and schizophrenia, in later life. Furthermore, early pharmacological intervention with D-serine may prevent the onset of psychosis in adult.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Serine racemase is associated with schizophrenia susceptibility in humans and in a mouse model.Hum Mol Genet. 2009 Sep 1;18(17):3227-43. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp261. Epub 2009 May 30. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19483194 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic disruption of DISC1-serine racemase binding elicits schizophrenia-like behavior via D-serine depletion.Mol Psychiatry. 2013 May;18(5):557-67. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.97. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Mol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 22801410 Free PMC article.
-
Auditory cognitive training improves prepulse inhibition in serine racemase mutant mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020 Aug;237(8):2499-2508. doi: 10.1007/s00213-020-05549-1. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32483676
-
[Analysis of mouse strain-dependent prepulse inhibition points to a role for Shmt1 (SHMT1) in mice and in schizophrenia].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2010 Nov;30(5-6):197-200. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 21226315 Review. Japanese.
-
The Role of Serine Racemase in the Pathophysiology of Brain Disorders.Adv Pharmacol. 2018;82:35-56. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2017.10.002. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Adv Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29413527 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal serine racemase associates with Disrupted-In-Schizophrenia-1 and DISC1 agglomerates: Implications for schizophrenia.Neurosci Lett. 2019 Jan 23;692:107-114. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.10.055. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Neurosci Lett. 2019. PMID: 30391323 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Early Intervention in Schizophrenia: Future Direction from Preclinical Findings.Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019 Jul 5;21(8):75. doi: 10.1007/s11920-019-1063-7. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2019. PMID: 31278495 Review.
-
The postnatal development of D-serine in the retinas of two mouse strains, including a mutant mouse with a deficiency in D-amino acid oxidase and a serine racemase knockout mouse.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Sep 17;5(9):848-54. doi: 10.1021/cn5000106. Epub 2014 Aug 1. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25083578 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation with D-serine prevents the onset of cognitive deficits in adult offspring after maternal immune activation.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 17;6:37261. doi: 10.1038/srep37261. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27853241 Free PMC article.
-
D-Serine and Serine Racemase Are Associated with PSD-95 and Glutamatergic Synapse Stability.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Feb 25;10:34. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00034. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26941605 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Javitt DC, Zukin SR (1991) Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 148: 1301–1308. - PubMed
-
- Krystal JH, D’Souza DC, Petrakis IL, Belger A, Berman RM, et al. (1999) NMDA agonists and antagonists as probes of glutamatergic dysfunction and pharmacotherapies in neuropsychiatric disorders. Harv Rev Psychiatry 7: 125–143. - PubMed
-
- Coyle JT, Tsai G (2004) The NMDA receptor glycine modulatory site: a therapeutic target for improving cognition and reducing negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 174: 32–38. - PubMed
-
- Javitt DC, Coyle JT (2004) Decoding schizophrenia. Sci Am 290: 48–55. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto K, Shimizu E, Iyo M (2005) Dysfunction of glia-neuron communication in pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Curr Psychiatry Rev 1: 151–163.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

