Anaplasma phagocytophilum inhibits apoptosis and promotes cytoskeleton rearrangement for infection of tick cells
- PMID: 23630955
- PMCID: PMC3697600
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00194-13
Anaplasma phagocytophilum inhibits apoptosis and promotes cytoskeleton rearrangement for infection of tick cells
Abstract
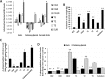
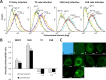
Anaplasma phagocytophilum causes human granulocytic anaplasmosis. Infection with this zoonotic pathogen affects gene expression in both the vertebrate host and the tick vector, Ixodes scapularis. Here, we identified new genes, including spectrin alpha chain or alpha-fodrin (CG8) and voltage-dependent anion-selective channel or mitochondrial porin (T2), that are involved in A. phagocytophilum infection/multiplication and the tick cell response to infection. The pathogen downregulated the expression of CG8 in tick salivary glands and T2 in both the gut and salivary glands to inhibit apoptosis as a mechanism to subvert host cell defenses and increase infection. In the gut, the tick response to infection through CG8 upregulation was used by the pathogen to increase infection due to the cytoskeleton rearrangement that is required for pathogen infection. These results increase our understanding of the role of tick genes during A. phagocytophilum infection and multiplication and demonstrate that the pathogen uses similar strategies to establish infection in both vertebrate and invertebrate hosts.
Figures



References
-
- de la Fuente J, Estrada-Peña A, Venzal JM, Kocan KM, Sonenshine DE. 2008. Overview: ticks as vectors of pathogens that cause disease in humans and animals. Front. Biosci. 13:6938–6946 - PubMed
-
- Dumler JS, Barbet AC, Bekker CPJ, Dasch GA, Palmer GH, Ray SC, Rikihisa Y, Rurangirwa FR. 2001. Reorganization of the genera in the families Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae in the order Rickettsiales: unification of some species of Ehrlichia with Anaplasma, Cowdria with Ehrlichia and Ehrlichia with Neorickettsia, descriptions of six new species combinations and designation of Ehrlichia equi and ‘HGE agent’ as subjective synonyms of Ehrlichia phagocytophila. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:2145–2165 - PubMed
-
- Stuen S. 2010. Anaplasma phagocytophilum—the most widespread tick-borne infection in animals in Europe. Vet. Res. Commun. 31:79–84 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

