Investigation of the function of Candida albicans Als3 by heterologous expression in Candida glabrata
- PMID: 23630968
- PMCID: PMC3697595
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00013-13
Investigation of the function of Candida albicans Als3 by heterologous expression in Candida glabrata
Abstract
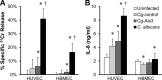
During hematogenously disseminated infection, blood-borne Candida albicans invades the endothelial cell lining of the vasculature to invade the deep tissues. Although the C. albicans Als3 invasin is critical for invasion and damage of endothelial cells in vitro, a C. albicans als3Δ/Δ mutant has normal virulence in the mouse model of disseminated infection. We hypothesized that the contribution of Als3 to virulence is obscured by the presence of additional C. albicans invasins. To elucidate the in vivo function of Als3, we heterologously expressed C. albicans ALS3 in Candida glabrata, a yeast that lacks a close ALS3 ortholog and has low virulence in mice. We found that following intravenous inoculation into mice, the ALS3-expressing strain preferentially trafficked to the brain, where it induced significantly elevated levels of myeloperoxidase, tumor necrosis factor, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, and gamma interferon. Also, the ALS3-expressing strain had enhanced adherence to and invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells in vitro, demonstrating a potential mechanism for ALS3-mediated neurotropism. In addition, upon initiation of infection, the ALS3-expressing strain had increased trafficking to the cortex of the kidneys. With prolonged infection, this strain persisted in the kidneys at significantly higher levels than the control strain but did not induce an elevated inflammatory response. Finally, the ALS3-expressing strain had increased resistance to neutrophil killing in vitro. These results indicate that during disseminated infection, Als3 mediates initial trafficking to the brain and renal cortex and contributes to fungal persistence in the kidneys.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of Candida albicans trafficking to the brain.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002305. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002305. Epub 2011 Oct 6. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21998592 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans adhesin Als3p is dispensable for virulence in the mouse model of disseminated candidiasis.Microbiology (Reading). 2011 Jun;157(Pt 6):1806-1815. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.046326-0. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Microbiology (Reading). 2011. PMID: 21436220 Free PMC article.
-
Als3 is a Candida albicans invasin that binds to cadherins and induces endocytosis by host cells.PLoS Biol. 2007 Mar;5(3):e64. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0050064. PLoS Biol. 2007. PMID: 17311474 Free PMC article.
-
Candida albicans Als3, a multifunctional adhesin and invasin.Eukaryot Cell. 2011 Feb;10(2):168-73. doi: 10.1128/EC.00279-10. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Eukaryot Cell. 2011. PMID: 21115738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungal invasion of epithelial cells.Microbiol Res. 2014 Nov;169(11):803-10. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2014.02.013. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Microbiol Res. 2014. PMID: 24670964 Review.
Cited by
-
Candida albicans White-Opaque Switching Influences Virulence but Not Mating during Oropharyngeal Candidiasis.Infect Immun. 2018 May 22;86(6):e00774-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00774-17. Print 2018 Jun. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 29581190 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast casein kinase 2 governs morphology, biofilm formation, cell wall integrity, and host cell damage of Candida albicans.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 6;12(11):e0187721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187721. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29107946 Free PMC article.
-
Functional regions of Candida albicans hyphal cell wall protein Als3 that determine interaction with the oral bacterium Streptococcus gordonii.Microbiology (Reading). 2015 Jan;161(Pt 1):18-29. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.083378-0. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Microbiology (Reading). 2015. PMID: 25332379 Free PMC article.
-
EphA2 is an epithelial cell pattern recognition receptor for fungal β-glucans.Nat Microbiol. 2018 Jan;3(1):53-61. doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0059-5. Epub 2017 Nov 13. Nat Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29133884 Free PMC article.
-
The NDV-3A vaccine protects mice from multidrug resistant Candida auris infection.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Aug 5;15(8):e1007460. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007460. eCollection 2019 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31381597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Phan QT, Fratti RA, Prasadarao NV, Edwards JE, Jr, Filler SG. 2005. N-cadherin mediates endocytosis of Candida albicans by endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 280:10455–10461 - PubMed
-
- Oh SH, Cheng G, Nuessen JA, Jajko R, Yeater KM, Zhao X, Pujol C, Soll DR, Hoyer LL. 2005. Functional specificity of Candida albicans Als3p proteins and clade specificity of ALS3 alleles discriminated by the number of copies of the tandem repeat sequence in the central domain. Microbiology 151:673–681 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

