Unusual cytochrome p450 enzymes and reactions
- PMID: 23632016
- PMCID: PMC3682512
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R113.462275
Unusual cytochrome p450 enzymes and reactions
Abstract
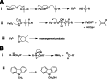
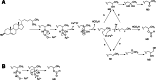
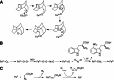
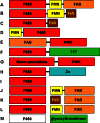
Cytochrome P450 enzymes primarily catalyze mixed-function oxidation reactions, plus some reductions and rearrangements of oxygenated species, e.g. prostaglandins. Most of these reactions can be rationalized in a paradigm involving Compound I, a high-valent iron-oxygen complex (FeO(3+)), to explain seemingly unusual reactions, including ring couplings, ring expansion and contraction, and fusion of substrates. Most P450s interact with flavoenzymes or iron-sulfur proteins to receive electrons from NAD(P)H. In some cases, P450s are fused to protein partners. Other P450s catalyze non-redox isomerization reactions. A number of permutations on the P450 theme reveal the diversity of cytochrome P450 form and function.
Keywords: Cytochrome P450; Enzyme Catalysis; Enzyme Mechanisms; Flavin; Heme; Natural Products; Oxidation-Reduction.
Figures
References
-
- Macdonald T. L., Zirvi K., Burka L. T., Peyman P., Guengerich F. P. (1982) Mechanism of cytochrome P-450 inhibition by cyclopropylamines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 104, 2050–2052
-
- Okazaki O., Guengerich F. P. (1993) Evidence for specific base catalysis in N-dealkylation reactions catalyzed by cytochrome P450 and chloroperoxidase. Differences in rates of deprotonation of aminium radicals as an explanation for high kinetic hydrogen isotope effects observed with peroxidases. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 1546–1552 - PubMed
-
- Ortiz de Montellano P. R., De Voss J. J. (2005) Substrate oxidation by cytochrome P450 enzymes. in Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry (Ortiz de Montellano P. R., ed) 3rd Ed., pp. 183–245, Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York
-
- Kedderis G. L., Dwyer L. A., Rickert D. E., Hollenberg P. F. (1983) Source of the oxygen atom in the product of cytochrome P-450-catalyzed N-demethylation reactions. Mol. Pharmacol. 23, 758–760 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 ES000267/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA090426/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- BB/G014329/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F00883X/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/F002521/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

