Folding of a cyclin box: linking multitarget binding to marginal stability, oligomerization, and aggregation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor AB pocket domain
- PMID: 23632018
- PMCID: PMC3696668
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.467316
Folding of a cyclin box: linking multitarget binding to marginal stability, oligomerization, and aggregation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor AB pocket domain
Abstract
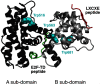
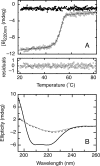
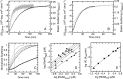
The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor (Rb) controls the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of cells in most eukaryotes with a role in the fate of stem cells. Its inactivation by mutation or oncogenic viruses is required for cellular transformation and eventually carcinogenesis. The high conservation of the Rb cyclin fold prompted us to investigate the link between conformational stability and ligand binding properties of the RbAB pocket domain. RbAB unfolding presents a three-state transition involving cooperative secondary and tertiary structure changes and a partially folded intermediate that can oligomerize. The first transition corresponds to unfolding of the metastable B subdomain containing the binding site for the LXCXE motif present in cellular and viral targets, and the second transition corresponds to the stable A subdomain. The low thermodynamic stability of RbAB translates into a propensity to rapidly oligomerize and aggregate at 37 °C (T50 = 28 min) that is suppressed by human papillomavirus E7 and E2F peptide ligands, suggesting that Rb is likely stabilized in vivo through binding to target proteins. We propose that marginal stability and associated oligomerization may be conserved for function as a "hub" protein, allowing the formation of multiprotein complexes, which could constitute a robust mechanism to retain its cell cycle regulatory role throughout evolution. Decreased stability and oligomerization are shared with the p53 tumor suppressor, suggesting a link between folding and function in these two essential cell regulators that are inactivated in most cancers and operate within multitarget signaling pathways.
Keywords: Cyclin Fold; Marginal Stability; Oligomerization; Protein Aggregation; Protein Folding; Protein Misfolding; Protein Stability; Retinoblastoma (Rb); Scaffold Proteins; Tumor Suppressor.
Figures
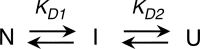







References
-
- van den Heuvel S., Dyson N. J. (2008) Conserved functions of the pRB and E2F families. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 713–724 - PubMed
-
- Khidr L., Chen P. L. (2006) RB, the conductor that orchestrates life, death and differentiation. Oncogene 25, 5210–5219 - PubMed
-
- Macaluso M., Montanari M., Giordano A. (2006) Rb family proteins as modulators of gene expression and new aspects regarding the interaction with chromatin remodeling enzymes. Oncogene 25, 5263–5267 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

