Rapid accumulation of endogenous tau oligomers in a rat model of traumatic brain injury: possible link between traumatic brain injury and sporadic tauopathies
- PMID: 23632019
- PMCID: PMC3675635
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.472746
Rapid accumulation of endogenous tau oligomers in a rat model of traumatic brain injury: possible link between traumatic brain injury and sporadic tauopathies
Abstract
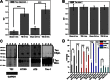
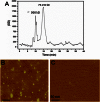
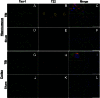
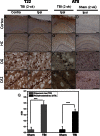
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a serious problem that affects millions of people in the United States alone. Multiple concussions or even a single moderate to severe TBI can also predispose individuals to develop a pathologically distinct form of tauopathy-related dementia at an early age. No effective treatments are currently available for TBI or TBI-related dementia; moreover, only recently has insight been gained regarding the mechanisms behind their connection. Here, we used antibodies to detect oligomeric and phosphorylated Tau proteins in a non-transgenic rodent model of parasagittal fluid percussion injury. Oligomeric and phosphorylated Tau proteins were detected 4 and 24 h and 2 weeks post-TBI in injured, but not sham control rats. These findings suggest that diagnostic tools and therapeutics that target only toxic forms of Tau may provide earlier detection and safe, more effective treatments for tauopathies associated with repetitive neurotrauma.
Keywords: Neurodegeneration; Protein Aggregation; Protein Assembly; Protein Misfolding; Tau; Tau Aggregation; Tau Oligomers; Tauopathies; Traumatic Brain Injury.
Figures


References
-
- Colicos M. A., Dixon C. E., Dash P. K. (1996) Delayed, selective neuronal death following experimental cortical impact injury in rats: possible role in memory deficits. Brain Res. 739, 111–119 - PubMed
-
- Smith D. H., Chen X. H., Pierce J. E., Wolf J. A., Trojanowski J. Q., Graham D. I., McIntosh T. K. (1997) Progressive atrophy and neuron death for one year following brain trauma in the rat. J. Neurotrauma 14, 715–727 - PubMed
-
- McKinney R. A., Debanne D., Gähwiler B. H., Thompson S. M. (1997) Lesion-induced axonal sprouting and hyperexcitability in the hippocampus in vitro: implications for the genesis of posttraumatic epilepsy. Nat. Med. 3, 990–996 - PubMed
-
- Pitkänen A., McIntosh T. K. (2006) Animal models of post-traumatic epilepsy. J. Neurotrauma 23, 241–261 - PubMed
-
- Behan L. A., Phillips J., Thompson C. J., Agha A. (2008) Neuroendocrine disorders after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 79, 753–759 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

