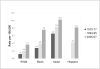Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: consider the population
- PMID: 23632345
- PMCID: PMC3683119
- DOI: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182872f29
Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: consider the population
Abstract
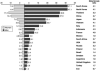
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is increasing in incidence and has a very high fatality rate. Cirrhosis due to chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis C is the leading risk factor for HCC. Global epidemiology of HCC is determined by the prevalence of dominant viral hepatitis and the age it is acquired in the underlying population. Upcoming risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. This review discusses the latest trends of HCC globally and in the United States. It also provides an evidence-based commentary on the risk factors and lists some of the preventive measures to reduce the incidence of HCC.
Figures
References
-
- GLOBOCAN International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) 2002 Available at: http://www-dep.iarc.fr.
-
- World Health Organization Mortality Database. WHO Statistical Information System. 2008 Available at: http://www.who.int/whosis.
-
- Bosch FX, Ribes J, Cleries R, Diaz M. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis. 2005;9:191–211. - PubMed
-
- Colombo M, de Franchis R, Del Ninno E, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in Italian patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:675–680. - PubMed
-
- Davila JA, El-Serag HB. The Rising Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the United States: an Update. Gastroenterology. 2012;142(suppl 1):S914–S914.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical