Metformin inhibits growth and enhances radiation response of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) through ATM and AMPK
- PMID: 23632475
- PMCID: PMC3670487
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.187
Metformin inhibits growth and enhances radiation response of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) through ATM and AMPK
Abstract
Background: We examined the potential of metformin (MET) to enhance non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) responses to ionising radiation (IR).
Methods: Human NSCLC cells, mouse embryonic fibroblasts from wild-type and AMP-activated kinase (AMPK) α1/2-subunit(-/-) embryos (AMPKα1/2(-/-)-MEFs) and NSCLC tumours grafted into Balb/c-nude mice were treated with IR and MET and subjected to proliferation, clonogenic, immunoblotting, cell cycle and apoptosis assays and immunohistochemistry (IHC).
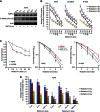
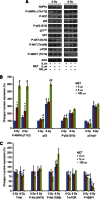
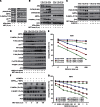
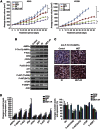
Results: Metformin (2.5 μM-5 mM) inhibited proliferation and radio-sensitised NSCLC cells. Metformin (i) activated the ataxia telengiectasia-mutated (ATM)-AMPK-p53/p21(cip1) and inhibited the Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-eIF4E-binding protein 1 (4EBP1) pathways, (ii) induced G1 cycle arrest and (iii) enhanced apoptosis. ATM inhibition blocked MET and IR activation of AMPK. Non-small cell lung cancer cells with inhibited AMPK and AMPKα1/2(-/-)-MEFs were resistant to the antiproliferative effects of MET and IR. Metformin or IR inhibited xenograft growth and combined treatment enhanced it further than each treatment alone. Ionising radiation and MET induced (i) sustained activation of ATM-AMPK-p53/p21(cip1) and inhibition of Akt-mTOR-4EBP1 pathways in tumours, (ii) reduced expression of angiogenesis and (iii) enhanced expression of apoptosis markers.
Conclusion: Clinically achievable MET doses inhibit NSCLC cell and tumour growth and sensitise them to IR. Metformin and IR mediate their action through an ATM-AMPK-dependent pathway. Our results suggest that MET can be a clinically useful adjunct to radiotherapy in NSCLC.
Figures


References
-
- Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Colosetti P, Auberger P, Tanti JF, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Bost F. The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene. 2008;27:3576–3586. - PubMed
-
- Bowker SL, Majumdar SR, Veugelers P, Johnson JA. Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin: Response to Farooki and Schneider. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:1990–1991. - PubMed
-
- Brachmann S, Fritsch C, Maira SM, Garcia-Echeverria C. PI3K and mTOR inhibitors: a new generation of targeted anticancer agents. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:194–198. - PubMed
-
- Bussink J, van der Kogel AJ, Kaanders JH. Activation of the PI3-K/AKT pathway and implications for radioresistance mechanisms in head and neck cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:288–296. - PubMed
-
- Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, Lum JJ, DeBerardinis RJ, Zhao F, Viollet B, Thompson CB. Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2007;67:6745–6752. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

