Intrahemispheric and interhemispheric structural network abnormalities in PLS and ALS
- PMID: 23633431
- PMCID: PMC6869498
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.22286
Intrahemispheric and interhemispheric structural network abnormalities in PLS and ALS
Abstract
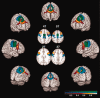
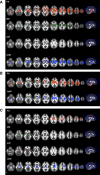
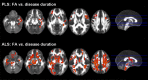
Using diffusion tensor (DT) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), damage to brain intrahemispheric and interhemispheric connections was assessed in 26 sporadic primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) patients compared with 28 sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patients with similar disability and 35 healthy controls. DT MRI diagnostic accuracy in distinguishing the two motor neuron disease (MND) variants was tested. PLS and ALS patients showed a distributed pattern of abnormalities of the motor system, including the corticospinal tracts and corpus callosum (CC). PLS versus ALS patients showed a more severe damage to the motor CC fibers and subcortical white matter (WM) underlying the primary motor cortices. Both patient groups showed an extra-motor damage, which was more severe in PLS. This did not appear to be driven by longer disease duration in PLS. In PLS patients, damage to the CC mid-body correlated with the severity of upper motor neuron clinical burden. CC fractional anisotropy values had the highest accuracy in distinguishing PLS from controls and ALS. PLS and ALS share an overlapped pattern of WM abnormalities. This underscores that PLS, despite its distinct clinical phenotype and long survival, still lies within the wider MND spectrum. Whether CC diffusivity may be a novel marker to increase confidence in an early diagnostic separation of PLS from ALS still needs to be investigated.
Keywords: DT MRI; VBM; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; brain atrophy; primary lateral sclerosis; white matter damage.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Agosta F, Scola E, Canu E, Marcone A, Magnani G, Sarro L, Copetti M, Caso F, Cerami C, Comi G, Cappa SF, Falini A, Filippi M (2012): White matter damage in frontotemporal lobar degeneration spectrum. Cerebral Cortex 22:2705–2714. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF, Richardson EP, Jr. (1981): Primary lateral sclerosis: A case report. Arch Neurol 38:630–633. - PubMed
-
- Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL (2000): El Escorial revisited: Revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1:293–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

