A randomized controlled trial of problem-solving therapy compared to cognitive therapy for the treatment of insomnia in adults
- PMID: 23633757
- PMCID: PMC3624829
- DOI: 10.5665/sleep.2640
A randomized controlled trial of problem-solving therapy compared to cognitive therapy for the treatment of insomnia in adults
Abstract
Study objectives: To compare the efficacy of problem-solving therapy (PST) combined with behavioral sleep strategies to standard cognitive therapy (CT) combined with behavioral sleep strategies in the treatment of insomnia.
Design: A six-week randomized controlled trial with one month follow-up.
Setting: The Australian National University Psychology Clinic, Canberra, Australia.
Participants: Forty-seven adults aged 18-60 years recruited from the community meeting the Research Diagnostic Criteria for insomnia.
Interventions: Participants received 6 weeks of treatment including one group session (sleep education and hygiene, stimulus control instructions and progressive muscle relaxation) followed by 5 weeks of individual treatment of PST or CT.
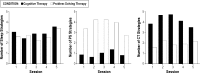
Measurements and results: Primary outcomes included sleep efficiency (SE) from sleep diaries, the Insomnia Severity Index (ISI), and the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). Secondary measures assessed dysfunctional sleep beliefs, problem-solving skills and orientations, and worry. Both treatments produced significant post therapy improvements in sleep which were maintained at 1 month follow-up (on SE Cohen d = 1.42, 95% CI 1.02-1.87 for PST; d = 1.26, 95% CI 0.81-1.65 for CT; on ISI d = 1.46, 95% CI 1.03-1.88 for PST; d = 1.95, 95% CI 0.52-2.38 for CT; for PSQI d = 0.97, 95% CI 0.55-1.40 for PST and d = 1.34, 95% CI 0.90-1.79 for the CT). There were no differences in PST and CT in the size or rate of improvement in sleep although CT produced a significant faster rate of decline in negative beliefs about sleep than PST and there was a trend (P = 0.08) for PST to produce a faster rate of improvement in negative problem orientation than CT.
Conclusions: The results provide preliminary support for problem solving treatment as an equally efficacious alternative component to cognitive therapy in psychological interventions for insomnia.
Keywords: Insomnia; cognitive behavior therapy; cognitive therapy; non-pharmacological treatment; problem-solving therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Morgenthaler T, Kramer M, Alessi C, et al. Practice parameters for the psychological and behavioral treatment of insomnia: an update. An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Report. Sleep. 2006;29:1415–9. - PubMed
-
- Morin CM, Bootzin RR, Buysse DJ, Edinger JD, Espie CA, Lichstein KL. Psychological and behavioral treatment of insomnia: update of the recent evidence (1998-2004) Sleep. 2006;29:1398–414. - PubMed
-
- Morin CM, Hauri PJ, Espie CA, Spielman AJ, Buysse DJ, Bootzin RR. Nonpharmacologic treatment of chronic insomnia: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine review. Sleep. 1999;22:1134–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical