Oxidative status in rat kidney exposed to petroleum hydrocarbons
- PMID: 23633852
- PMCID: PMC3633267
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-9668.107280
Oxidative status in rat kidney exposed to petroleum hydrocarbons
Abstract
Objective: The study investigates the possible role of oxidative stress on renal tissues in association with petroleum hydrocarbon-induced nephrotoxicity.
Materials and methods: Rats of comparable weights were randomly distributed into 10 groups: Control and groups exposed to kerosene, petrol, and diesel via inhalation, contamination by food, and contamination by water. The exposure lasted for eight weeks.
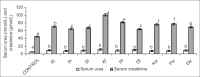
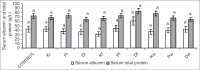
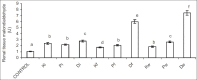
Results: Exposure to petroleum hydrocarbon led to significant rise in serum urea and creatinine, and renal tissue malondialdehyde. It also caused significant reduction in urinary urea and creatinine, and reduced glutathione, superoxide dismutase, and catalase activities of renal tissue homogenate. However, serum and urine concentrations of albumin and total protein were comparable in all groups.
Conclusion: Results from this study shows that exposure to petroleum hydrocarbon led to renal dysfunction via oxidative stress, increasing lipid peroxidation and reducing the antioxidant defense mechanism.
Keywords: Diesel; kerosene; oxidative stress; petrol; renal function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



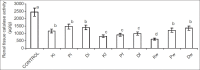

References
-
- Edwards CW. Toxicology of oil field waste hazards to livestock associated with the petroleum industry. Vet Clin North Am. 1989;5:363–74. - PubMed
-
- Coppock RW, Mostrom MS, Khan A, Semalula SS. Toxicology of oil field pollutants in cattle: A review. Vet Hum Toxicol. 1995;37:369–576. - PubMed
-
- Kato M, Rocha ML, Carvallio AB, Chares ME, Rana MC, Oliverira FC. Occupational exposure to neurotoxicants; preliminary survey in five industries of Camacari petrochemical complex, Brazil. Environ Res. 1996;136:49–56. - PubMed
-
- Uboh FE, Akpanabiatu MI, Ndem JI, Alozie Y, Ebong PE. Comparative nephrotoxic effect associated with exposure to diesel and gasoline vapours in rats. J Toxicol Environ Health Sci. 2009;1:68–74.
-
- Aboutabl ME, Zordoky BN, Hammock BD, El-Kadi AO. Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase confers cardioprotection and prevents cardiac cytochrome P450 induction by benzo (a) pyrene. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011;57:273–81. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
