Genome-Wide RNAi Longevity Screens in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 23633911
- PMCID: PMC3468884
- DOI: 10.2174/138920212803251391
Genome-Wide RNAi Longevity Screens in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
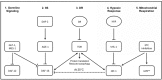
Progress in aging research has identified genetic and environmental factors that regulate longevity across species. The nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans is a genetically tractable model system that has been widely used to investigate the molecular mechanisms of aging, and the development of RNA interference (RNAi) technology has provided a powerful tool for performing large-scale genetic screens in this organism. Genome-wide screens have identified hundreds of genes that influence lifespan, many of which fall into distinct functional classes and pathways. The purpose of this review is to summarize the results of large-scale RNAi longevity screens in C. elegans, and to provide an in-depth comparison and analysis of their methodology and most significant findings.
Keywords: Dietary restriction; FOXO; Genomic; IGF-1; Insulin; Longevity; Mitochondria..
Figures
References
-
- Kenyon CJ. The genetics of ageing. Nature. 2010;464(7288):504–12. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
