The Chlamydia pneumoniae invasin protein Pmp21 recruits the EGF receptor for host cell entry
- PMID: 23633955
- PMCID: PMC3635982
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003325
The Chlamydia pneumoniae invasin protein Pmp21 recruits the EGF receptor for host cell entry
Abstract
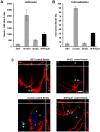
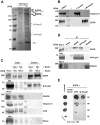
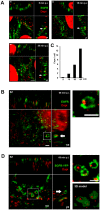
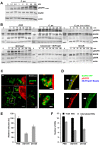
Infection of mammalian cells by the strictly intracellular pathogens Chlamydiae requires adhesion and internalization of the infectious Elementary Bodies (EBs). The components of the latter step were unknown. Here, we identify Chlamydia pneumoniae Pmp21 as an invasin and EGFR as its receptor. Modulation of EGFR surface expression evokes correlated changes in EB adhesion, internalization and infectivity. Ectopic expression of EGFR in EGFR-negative hamster cells leads to binding of Pmp21 beads and EBs, thus boosting the infection. EB/Pmp21 binding and invasion of epithelial cells results in activation of EGFR, recruitment of adaptors Grb2 and c-Cbl and activation of ERK1/2, while inhibition of EGFR or MEK kinase activity abrogates EB entry, but not attachment. Binding of Grb2 and c-Cbl by EGFR is essential for infection. This is the first report of an invasin-receptor interaction involved in host-cell invasion by any chlamydial species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Campbell LA, Kuo CC (2004) Chlamydia pneumoniae–an infectious risk factor for atherosclerosis? Nat Rev Microbiol 2: 23–32. - PubMed
-
- Boleti H, Benmerah A, Ojcius DM, Cerf-Bensussan N, Dautry-Varsat A (1999) Chlamydia infection of epithelial cells expressing dynamin and Eps15 mutants: clathrin-independent entry into cells and dynamin-dependent productive growth. J Cell Sci 112: 1487–1496. - PubMed
-
- Dautry-Varsat A, Subtil A, Hackstadt T (2005) Recent insights into the mechanisms of Chlamydia entry. Cell Microbiol 7: 1714–1722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

