Reciprocal complementation of the tumoricidal effects of radiation and natural killer cells
- PMID: 23634213
- PMCID: PMC3636248
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061797
Reciprocal complementation of the tumoricidal effects of radiation and natural killer cells
Abstract
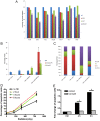
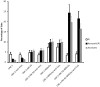
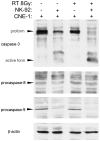
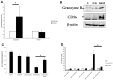
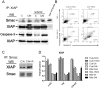
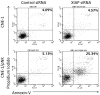
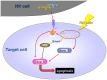
The tumor microenvironment is a key determinant for radio-responsiveness. Immune cells play an important role in shaping tumor microenvironments; however, there is limited understanding of how natural killer (NK) cells can enhance radiation effects. This study aimed to assess the mechanism of reciprocal complementation of radiation and NK cells on tumor killing. Various tumor cell lines were co-cultured with human primary NK cells or NK cell line (NK-92) for short periods and then exposed to irradiation. Cell proliferation, apoptosis and transwell assays were performed to assess apoptotic efficacy and cell viability. Western blot analysis and immunoprecipitation methods were used to determine XIAP (X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein) and Smac (second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase) expression and interaction in tumor cells. Co-culture did not induce apoptosis in tumor cells, but a time- and dose-dependent enhancing effect was found when co-cultured cells were irradiated. A key role for caspase activation via perforin/granzyme B (Grz B) after cell-cell contact was determined, as the primary radiation enhancing effect. The efficacy of NK cell killing was attenuated by upregulation of XIAP to bind caspase-3 in tumor cells to escape apoptosis. Knockdown of XIAP effectively potentiated NK cell-mediated apoptosis. Radiation induced Smac released from mitochondria and neutralized XIAP and therefore increased the NK killing. Our findings suggest NK cells in tumor microenvironment have direct radiosensitization effect through Grz B injection while radiation enhances NK cytotoxicity through triggering Smac release.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase (SMAC) mimetic potentiates tumor susceptibility toward natural killer cell-mediated killing.Leuk Lymphoma. 2014 Mar;55(3):645-51. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.807925. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014. PMID: 23697877
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) blocks Apo2 ligand/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis of prostate cancer cells in the presence of mitochondrial activation: sensitization by overexpression of second mitochondria-derived activator of caspase/direct IAP-binding protein with low pl (Smac/DIABLO).Mol Cancer Ther. 2002 Oct;1(12):1051-8. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002. PMID: 12481428
-
Bax/Bak-dependent, Drp1-independent Targeting of X-linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (XIAP) into Inner Mitochondrial Compartments Counteracts Smac/DIABLO-dependent Effector Caspase Activation.J Biol Chem. 2015 Sep 4;290(36):22005-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.643064. Epub 2015 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26134559 Free PMC article.
-
Combined use of NK cells and radiotherapy in the treatment of solid tumors.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 9;14:1306534. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1306534. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38264648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unleashing the power of NK cells in anticancer immunotherapy.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Mar;100(3):337-349. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02120-z. Epub 2021 Aug 9. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 34374809 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiotherapy induced immunogenic cell death by remodeling tumor immune microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 1;13:1074477. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1074477. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36532071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Radiation on the Tumor Microenvironment.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2020 Apr;30(2):145-157. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2019.12.004. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32381294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D tumor spheroid microarray for high-throughput, high-content natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity.Commun Biol. 2021 Jul 21;4(1):893. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02417-2. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34290356 Free PMC article.
-
Local irradiation does not enhance the effect of immunostimulatory AdCD40L gene therapy combined with low dose cyclophosphamide in melanoma patients.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 31;8(45):78573-78587. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19750. eCollection 2017 Oct 3. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29108250 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-ray irradiation modulates PGRMC1 expression and the number of CD56+ and FoxP3+ cells in the tumor microenvironment of endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma.Radiat Oncol J. 2021 Dec;39(4):324-333. doi: 10.3857/roj.2021.00472. Epub 2021 Aug 17. Radiat Oncol J. 2021. PMID: 34986554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chi KH, Wang YS, Kao SJ (2012) Improving radioresponse through modification of the tumor immunological microenvironment. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 27: 6–11. - PubMed
-
- Grabenbauer GG, Lahmer G, Distel L, Niedobitek G (2006) Tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T cells but not regulatory T cells predict outcome in anal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 12: 3355–3360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

