Complexity in cancer biology: is systems biology the answer?
- PMID: 23634284
- PMCID: PMC3639655
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.62
Complexity in cancer biology: is systems biology the answer?
Abstract
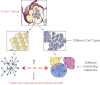
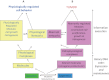
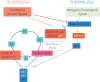
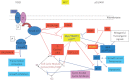
Complex phenotypes emerge from the interactions of thousands of macromolecules that are organized in multimolecular complexes and interacting functional modules. In turn, modules form functional networks in health and disease. Omics approaches collect data on changes for all genes and proteins and statistical analysis attempts to uncover the functional modules that perform the functions that characterize higher levels of biological organization. Systems biology attempts to transcend the study of individual genes/proteins and to integrate them into higher order information. Cancer cells exhibit defective genetic and epigenetic networks formed by altered complexes and network modules arising in different parts of tumor tissues that sustain autonomous cell behavior which ultimately lead tumor growth. We suggest that an understanding of tumor behavior must address not only molecular but also, and more importantly, tumor cell heterogeneity, by considering cancer tissue genetic and epigenetic networks, by characterizing changes in the types, composition, and interactions of complexes and networks in the different parts of tumor tissues, and by identifying critical hubs that connect them in time and space.
Keywords: Cell cycle; complex; cyclin-dependent kinase; cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors signaling; module; network; oncogene; oncoprotein; system; tumor suppressor gene; tumor suppressor protein.
Figures
References
-
- Ideker T, Galitski T, Hood L. A new approach to decoding life: systems biology. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2001;2:343–372. - PubMed
-
- Goh CS, et al. Mining the structural genomics pipeline: identification of protein properties that affect high-throughput experimental analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2004;336:115–130. - PubMed
-
- Lan N, Montelione GT, Gerstein M. Ontologies for proteomics: towards a systematic definition of structure and function that scales to the genome level. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003;7:44–54. - PubMed
-
- Brent R. Genomic biology. Cell. 2000;100:169–183. - PubMed
-
- Clarke PA, et al. Gene expression microarray analysis in cancer biology, pharmacology, and drug development: progress and potential. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2001;62:1311–1336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

