Identification of potential biomarkers from microarray experiments using multiple criteria optimization
- PMID: 23634293
- PMCID: PMC3639664
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.69
Identification of potential biomarkers from microarray experiments using multiple criteria optimization
Abstract
Microarray experiments are capable of determining the relative expression of tens of thousands of genes simultaneously, thus resulting in very large databases. The analysis of these databases and the extraction of biologically relevant knowledge from them are challenging tasks. The identification of potential cancer biomarker genes is one of the most important aims for microarray analysis and, as such, has been widely targeted in the literature. However, identifying a set of these genes consistently across different experiments, researches, microarray platforms, or cancer types is still an elusive endeavor. Besides the inherent difficulty of the large and nonconstant variability in these experiments and the incommensurability between different microarray technologies, there is the issue of the users having to adjust a series of parameters that significantly affect the outcome of the analyses and that do not have a biological or medical meaning. In this study, the identification of potential cancer biomarkers from microarray data is casted as a multiple criteria optimization (MCO) problem. The efficient solutions to this problem, found here through data envelopment analysis (DEA), are associated to genes that are proposed as potential cancer biomarkers. The method does not require any parameter adjustment by the user, and thus fosters repeatability. The approach also allows the analysis of different microarray experiments, microarray platforms, and cancer types simultaneously. The results include the analysis of three publicly available microarray databases related to cervix cancer. This study points to the feasibility of modeling the selection of potential cancer biomarkers from microarray data as an MCO problem and solve it using DEA. Using MCO entails a new optic to the identification of potential cancer biomarkers as it does not require the definition of a threshold value to establish significance for a particular gene and the selection of a normalization procedure to compare different experiments is no longer necessary.
Keywords: Cancer biomarkers; cervical cancer; data envelopment analysis; microarray data analysis; multiple criteria optimization.
Figures

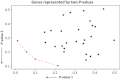
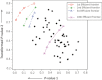
References
-
- Ho L, Sharma N, Blackman L, Festa E, Reddy G, Pasinetti GM. From proteomics to biomarker discovery in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. Rev. 2005;48:360–369. - PubMed
-
- Di Valentin E, Crahay C, Garbacki N, Hennuy B, Guéders M, Noël A, et al. New asthma biomarkers: lessons from murine models of acute and chronic asthma. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2009;296:L185–L197. - PubMed
-
- Ioannidis JP, Allison DB, Ball CA, Coulibaly I, Cui X, Culhane AC, et al. Repeatability of published microarray gene expression analyses. Nat. Genet. 2009;41:149–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

