Development of an HPLC-UV Method for the Analysis of Drugs Used for Combined Hypertension Therapy in Pharmaceutical Preparations and Human Plasma
- PMID: 23634320
- PMCID: PMC3619551
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/179627
Development of an HPLC-UV Method for the Analysis of Drugs Used for Combined Hypertension Therapy in Pharmaceutical Preparations and Human Plasma
Abstract
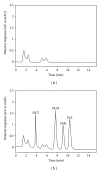
A simple, rapid, and selective HPLC-UV method was developed for the determination of antihypertensive drug substances: amlodipine besilat (AML), olmesartan medoxomil (OLM), valsartan (VAL), and hydrochlorothiazide (HCT) in pharmaceuticals and plasma. These substances are mostly used as combinations. The combinations are found in various forms, especially in current pharmaceuticals as threesome components: OLM, AML, and HCT (combination I) and AML, VAL, and HCT (combination II). The separation was achieved by using an RP-CN column, and acetonitrile-methanol-10 mmol orthophosphoric acid pH 2.5 (7 : 13 : 80, v/v/v) was used as a mobile phase; the detector wavelength was set at 235 nm. The linear ranges were found as 0.1-18.5 μ g/mL, 0.4-25.6 μ g/mL, 0.3-15.5 μ g/mL, and 0.3-22 μ g/mL for AML, OLM, VAL, and HCT, respectively. In order to check the selectivity of the method for pharmaceutical preparations, forced degradation studies were carried out. According to the validation studies, the developed method was found to be reproducible and accurate as shown by RSD ≤6.1%, 5.7%, 6.9%, and 4.6% and relative mean error (RME) ≤10.6%, 5.8%, 6.5%, and 6.8% for AML, OLM, VAL, and HCT, respectively. Consequently, the method was applied to the analysis of tablets and plasma of the patients using drugs including those substances.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Novel Pure Component Contribution Algorithm (PCCA) and UHPLC Methods for Separation and Quantification of Amlodipine, Valsartan, and Hydrochlorothiazide in Ternary Mixture.J AOAC Int. 2017 May 1;100(3):692-699. doi: 10.5740/jaoacint.16-0195. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J AOAC Int. 2017. PMID: 28118578
-
Simple RP-HPLC method for determination of triple drug combination of valsartan, amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide in human plasma.Acta Pharm. 2012 Mar;62(1):45-58. doi: 10.2478/v10007-012-0004-3. Acta Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22472448
-
Development and validation of a stability-indicating UPLC method for the determination of olmesartan medoxomil, amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide degradation impurities in their triple-combination dosage form using factorial design of experiments.Biomed Chromatogr. 2021 Nov;35(11):e5194. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5194. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Biomed Chromatogr. 2021. PMID: 34110035
-
Antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan medoxomil or valsartan in combination with amlodipine: a review of factorial-design studies.Curr Med Res Opin. 2009 Jan;25(1):177-85. doi: 10.1185/03007990802597456. Curr Med Res Opin. 2009. PMID: 19210150 Review.
-
Blood pressure control with angiotensin receptor blocker-based three-drug combinations: key trials.Adv Ther. 2012 May;29(5):401-15. doi: 10.1007/s12325-012-0019-7. Epub 2012 May 17. Adv Ther. 2012. PMID: 22610686 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Validation of a LC-MS/MS Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Amlodipine and Valsartan in Human Plasma: Application to a Bioequivalence Study.Sci Pharm. 2014 Mar 26;82(3):585-600. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1402-11. Print 2014 Jul-Sep. Sci Pharm. 2014. PMID: 25853070 Free PMC article.
-
Application of an LC-MS/MS method for the analysis of amlodipine, valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide in polypill for a bioequivalence study.J Pharm Anal. 2017 Oct;7(5):309-316. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 4. J Pharm Anal. 2017. PMID: 29404054 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of hydrolysis of olmesartan medoxomil in different pH buffers by simultaneously measuring olmesartan medoxomil and olmesartan.PLoS One. 2025 May 2;20(5):e0321142. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321142. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40315202 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. The Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217–223. - PubMed
-
- Kjeldsen SE, Jamerson KA, Bakris GL, et al. Predictors of blood pressure response to intensified and fixed combination treatment of hypertension: the ACCOMPLISH study. Blood Pressure. 2008;17(1):7–17. - PubMed
-
- Jamerson KA, Bakris GL, Dahlö B, et al. Exceptional early blood pressure control rates: the ACCOMPLISH trial. Blood Pressure. 2007;16(2):80–86. - PubMed
-
- White WB, Giles T, Bakris GL, Neutel JM, Davidai G, Weber MA. Measuring the efficacy of antihypertensive therapy by ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in the primary care setting. American Heart Journal. 2006;151(1):176–184. - PubMed
-
- Budavari S. The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs and Biologicals. 13th edition. Merck and Co.: Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA; 2001.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

