RHD variants in Polish blood donors routinely typed as D-
- PMID: 23634715
- PMCID: PMC5497842
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.12230
RHD variants in Polish blood donors routinely typed as D-
Abstract
Background: Blood donors exhibiting a weak D or DEL phenotypical expression may be mistyped D- by standard serology hence permitting incompatible transfusion to D- recipients. Molecular methods may overcome these technical limits. Our aim was to estimate the frequency of RHD alleles among the apparently D- Polish donor population and to characterize its molecular background.
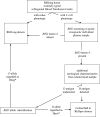
Study design and methods: Plasma pools collected from 31,200 consecutive Polish donors typed as D- were tested by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for the presence of RHD-specific markers located in Intron 4 and Exons 7 and 10. RHD+ individuals were characterized by PCR or cDNA sequencing and serology.
Results: Plasma cross-pool strategy revealed 63 RHD+ donors harboring RHD*01N.03 (n = 17), RHD*15 (n = 12), RHD*11 (n = 7), RHD*DEL8 (n = 3), RHD*01W.2 (n = 3), RHD-CE(10) (n = 3), RHD*01W.3, RHD*01W.9, RHD*01N.05, RHD*01N.07, RHD*01N.23, and RHD(IVS1-29G>C) and two novel alleles, RHD*(767C>G) (n = 3) and RHD*(1029C>A). Among 47 cases available for serology, 27 were shown to express the D antigen
Conclusion: 1) Plasma cross-pool strategy is a reliable and cost-effective tool for RHD screening. 2) Only 0.2% of D- Polish donors carry some fragments of the RHD gene; all of them were C or E+. 3) Almost 60% of the detected RHD alleles may be potentially immunogenic when transfused to a D- recipient.
© 2013 American Association of Blood Banks.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest relevant to this publication.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of RHD alleles with the potential of anti-D immunization among seemingly D- blood donors in Upper Austria.Transfusion. 2009 Apr;49(4):676-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.2008.02046.x. Epub 2009 Jan 2. Transfusion. 2009. PMID: 19170995
-
Molecular basis for D- Japanese: identification of novel DEL and D- alleles.Vox Sang. 2015 Nov;109(4):359-65. doi: 10.1111/vox.12290. Epub 2015 May 7. Vox Sang. 2015. PMID: 25953588
-
RHD variants in Flanders, Belgium.Transfusion. 2015 Jun;55(6 Pt 2):1411-7. doi: 10.1111/trf.12947. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Transfusion. 2015. PMID: 25413499
-
Serological weak D phenotypes: a review and guidance for interpreting the RhD blood type using the RHD genotype.Br J Haematol. 2017 Oct;179(1):10-19. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14757. Epub 2017 May 16. Br J Haematol. 2017. PMID: 28508413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular RHD screening of RhD negative donors can replace standard serological testing for RhD negative donors.Transfus Apher Sci. 2014 Apr;50(2):163-8. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Transfus Apher Sci. 2014. PMID: 24656493 Review.
Cited by
-
A preliminary evaluation of next-generation sequencing as a screening tool for targeted genotyping of erythrocyte and platelet antigens in blood donors.Blood Transfus. 2018 May;16(3):285-292. doi: 10.2450/2017.0253-16. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Blood Transfus. 2018. PMID: 28287381 Free PMC article.
-
14 Years of Polish Experience in Non-Invasive Prenatal Blood Group Diagnosis.Transfus Med Hemother. 2015 Nov;42(6):361-4. doi: 10.1159/000440821. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Transfus Med Hemother. 2015. PMID: 26733766 Free PMC article.
-
Impact on patient of the detection of weakly expressed RhD antigens in blood donors.Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter. 2015 Sep-Oct;37(5):290-1. doi: 10.1016/j.bjhh.2015.07.007. Epub 2015 Aug 5. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter. 2015. PMID: 26408360 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
RHD-Positive Alleles among D- C/E+ Individuals from India.Transfus Med Hemother. 2018 May;45(3):173-177. doi: 10.1159/000479239. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Transfus Med Hemother. 2018. PMID: 29928172 Free PMC article.
-
Single-exon fetal RHD genotyping: a 31-month follow up in the obstetric population of Western Sweden.Blood Transfus. 2024 Sep;22(5):387-394. doi: 10.2450/BloodTransfus.741. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Blood Transfus. 2024. PMID: 38814881 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

