Motivated behaviors and levels of 3α,5α-THP in the midbrain are attenuated by knocking down expression of pregnane xenobiotic receptor in the midbrain ventral tegmental area of proestrous rats
- PMID: 23634744
- PMCID: PMC3700579
- DOI: 10.1111/jsm.12173
Motivated behaviors and levels of 3α,5α-THP in the midbrain are attenuated by knocking down expression of pregnane xenobiotic receptor in the midbrain ventral tegmental area of proestrous rats
Abstract
Introduction: Progesterone (P4 ) and its product, 5α-pregnan-3α-ol-20-one (3α,5α-THP), act in the midbrain ventral tegmental area (VTA) to alter motivated behaviors, such as mating, and motor and anxiety behavior. Of interest is whether 3α,5α-THP formation requires the pregnane xenobiotic receptor (PXR), which is expressed in the midbrain of rats.
Aim: The role of PXR in the midbrain for 3α,5α-THP formation, which precedes modulation of motivated behaviors, was investigated.
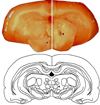
Methods: Rats had estrous cycle phase determined and were assessed when they were in diestrus or proestrus. Diestrous and proestrous rats were infused with control or antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotides (AS-ODNs) targeted against PXR to the VTA.
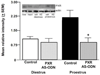
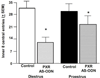
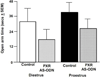
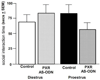
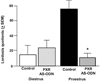
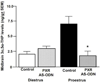
Main outcome measures: In pilot studies, PXR gene and protein expression in the midbrain were determined with quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting, respectively. Diestrous and proestrous rats infused with control or AS-ODNs to the VTA were tested for anxiety (open field and plus maze), social (social interaction), and sexual (paced mating) behavior. Expression of PXR in the midbrain was verified with Western blotting. Plasma estradiol, P4 , dihydroprogesterone (DHP), and 3α,5α-THP levels, and brain P4 , DHP, and 3α,5α-THP levels were measured. We predicted that proestrous rats infused with PXR AS-ODNs would have decreased anti-anxiety, social, and sexual behavior, lower midbrain expression of PXR, and lower midbrain levels of 3α,5α-THP compared with controls.
Results: Results supported the hypothesis that formation of 3α,5α-THP requires PXR and may be important for motivated behaviors. PXR AS-ODN, compared with control, infusions to the VTA reduced PXR expression and 3α,5α-THP levels in the midbrain and attenuated sexual receptivity of proestrous rats.
Conclusions: Knockdown of PXR in the midbrain reduces 3α,5α-THP levels and sexual receptivity of proestrous rats. Thus, PXR in the midbrain may be required for the observed increase in 3α-5α-THP during proestrus, which has subsequent effects on motivated, reproductive behaviors.
Keywords: Allopregnanolone; Lordosis; Mating; Neurosteroids; Progesterone; Receptivity.
© 2013 International Society for Sexual Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of pregnane xenobiotic receptor in the midbrain ventral tegmental area for estradiol- and 3α,5α-THP-facilitated lordosis of female rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Sep;231(17):3365-74. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3406-0. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24435323 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of pregnane xenobiotic receptor in mating-induced allopregnanolone formation in the midbrain and hippocampus and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hippocampus among female rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Sep;231(17):3375-90. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3569-3. Epub 2014 May 1. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24781516 Free PMC article.
-
Infusions of 3alpha,5alpha-THP to the VTA enhance exploratory, anti-anxiety, social, and sexual behavior and increase levels of 3alpha,5alpha-THP in midbrain, hippocampus, diencephalon, and cortex of female rats.Behav Brain Res. 2008 Feb 11;187(1):88-99. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2007.08.031. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Behav Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 17919744 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnane xenobiotic receptors and membrane progestin receptors: role in neurosteroid-mediated motivated behaviours.J Neuroendocrinol. 2013 Nov;25(11):1002-11. doi: 10.1111/jne.12105. J Neuroendocrinol. 2013. PMID: 24028379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel substrates for, and sources of, progestogens for reproduction.J Neuroendocrinol. 2011 Nov;23(11):961-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2011.02180.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21696472 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurosteroidogenesis Today: Novel Targets for Neuroactive Steroid Synthesis and Action and Their Relevance for Translational Research.J Neuroendocrinol. 2016 Feb;28(2):12351. doi: 10.1111/jne.12351. J Neuroendocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26681259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase 0 of the Xenobiotic Response: Nuclear Receptors and Other Transcription Factors as a First Step in Protection from Xenobiotics.Nucl Receptor Res. 2019;6:101447. doi: 10.32527/2019/101447. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Nucl Receptor Res. 2019. PMID: 31815118 Free PMC article.
-
The pregnane xenobiotic receptor, a prominent liver factor, has actions in the midbrain for neurosteroid synthesis and behavioral/neural plasticity of female rats.Front Syst Neurosci. 2014 Apr 21;8:60. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2014.00060. eCollection 2014. Front Syst Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24795576 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased allopregnanolone induced by hormonal contraceptives is associated with a reduction in social behavior and sexual motivation in female rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Sep;231(17):3351-64. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3539-9. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24728651
-
Role of pregnane xenobiotic receptor in the midbrain ventral tegmental area for estradiol- and 3α,5α-THP-facilitated lordosis of female rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014 Sep;231(17):3365-74. doi: 10.1007/s00213-013-3406-0. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24435323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frye CA. Neurosteroids-From Basic Research to Clinical Perspectives. In: Rubin Robert T, Pfaff Donald W., editors. Hormones/Behavior Relations of Clinical Importance. San Diego: Academic Press; 2009. pp. 395–416.
-
- Frye CA, Bayon LE, Pursnani NK, Purdy RH. The neurosteroids, progesterone and 3α,5α-THP, enhance sexual motivation, receptivity, and proceptivity in female rats. Brain Res. 1998;808:72–83. - PubMed
-
- Frye CA, Petralia SM, Rhodes ME. Estrous cycle and sex differences in performance on anxiety tasks coincide with increases in hippocampal progesterone and 3α,5α-THP. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000;67:587–596. - PubMed
-
- Holzbauer M. Physiological variations in the ovarian production of 5α-pregnane derivatives with sedative properties in the rat. J Steroid Biochem. 1975;6:1307–1310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

