Extranuclear ERα is associated with regression of T47D PKCα-overexpressing, tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer
- PMID: 23634843
- PMCID: PMC3661391
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-34
Extranuclear ERα is associated with regression of T47D PKCα-overexpressing, tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note to: Extranuclear ERα is associated with regression of T47D PKCα-overexpressing, tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jul 17;16(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0697-5. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28716023 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
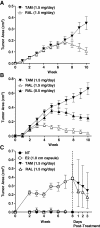
Background: Prior to the introduction of tamoxifen, high dose estradiol was used to treat breast cancer patients with similar efficacy as tamoxifen, albeit with some undesirable side effects. There is renewed interest to utilize estradiol to treat endocrine resistant breast cancers, especially since findings from several preclinical models and clinical trials indicate that estradiol may be a rational second-line therapy in patients exhibiting resistance to tamoxifen and/or aromatase inhibitors. We and others reported that breast cancer patients bearing protein kinase C alpha (PKCα)- expressing tumors exhibit endocrine resistance and tumor aggressiveness. Our T47D:A18/PKCα preclinical model is tamoxifen-resistant, hormone-independent, yet is inhibited by 17β-estradiol (E2) in vivo. We previously reported that E2-induced T47D:A18/PKCα tumor regression requires extranuclear ERα and interaction with the extracellular matrix.
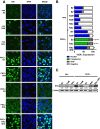
Methods: T47D:A18/PKCα cells were grown in vitro using two-dimensional (2D) cell culture, three-dimensional (3D) Matrigel and in vivo by establishing xenografts in athymic mice. Immunofluoresence confocal microscopy and co-localization were applied to determine estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) subcellular localization. Co-immunoprecipitation and western blot were used to examine interaction of ERα with caveolin-1.
Results: We report that although T47D:A18/PKCα cells are cross-resistant to raloxifene in cell culture and in Matrigel, raloxifene induces regression of tamoxifen-resistant tumors. ERα rapidly translocates to extranuclear sites during T47D:A18/PKCα tumor regression in response to both raloxifene and E2, whereas ERα is primarily localized in the nucleus in proliferating tumors. E2 treatment induced complete tumor regression whereas cessation of raloxifene treatment resulted in tumor regrowth accompanied by re-localization of ERα to the nucleus. T47D:A18/neo tumors that do not overexpress PKCα maintain ERα in the nucleus during tamoxifen-mediated regression. An association between ERα and caveolin-1 increases in tumors regressing in response to E2.
Conclusions: Extranuclear ERα plays a role in the regression of PKCα-overexpressing tamoxifen-resistant tumors. These studies underline the unique role of extranuclear ERα in E2- and raloxifene-induced tumor regression that may have implications for treatment of endocrine-resistant PKCα-expressing tumors encountered in the clinic.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Novel antitumor effect of estradiol in athymic mice injected with a T47D breast cancer cell line overexpressing protein kinase Calpha.Clin Cancer Res. 2001 Oct;7(10):3156-65. Clin Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11595710
-
Overexpression of PKCalpha is required to impart estradiol inhibition and tamoxifen-resistance in a T47D human breast cancer tumor model.Carcinogenesis. 2006 Aug;27(8):1538-46. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgl002. Epub 2006 Mar 2. Carcinogenesis. 2006. PMID: 16513679
-
Novel selective estrogen mimics for the treatment of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2014 Nov;13(11):2515-26. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0319. Epub 2014 Sep 9. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014. PMID: 25205655 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Estrogen Receptors and p53: A Broader Role for Tamoxifen?Endocrinology. 2025 Feb 5;166(3):bqaf020. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaf020. Endocrinology. 2025. PMID: 39891710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk of methylation and tamoxifen in breast cancer (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 Oct;30(4):180. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13304. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39129315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential expression of estrogen receptor subtypes and variants in ovarian cancer: effects on cell invasion, proliferation and prognosis.BMC Cancer. 2017 Aug 31;17(1):606. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3601-1. BMC Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28859612 Free PMC article.
-
The new biology of estrogen-induced apoptosis applied to treat and prevent breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015 Feb;22(1):R1-31. doi: 10.1530/ERC-14-0448. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25339261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Selective Estrogen Receptor Downregulators (SERDs) Developed against Treatment-Resistant Breast Cancer.J Med Chem. 2017 Feb 23;60(4):1325-1342. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01355. Epub 2017 Feb 10. J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28117994 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of estrogen receptor-associated hub genes and potential molecular mechanisms in non-smoking females with lung adenocarcinoma using integrated bioinformatics analysis.Oncol Lett. 2019 Nov;18(5):4605-4612. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10845. Epub 2019 Sep 10. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31611968 Free PMC article.
-
Retraction Note to: Extranuclear ERα is associated with regression of T47D PKCα-overexpressing, tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jul 17;16(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0697-5. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28716023 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

