Telomere-homologous G-rich oligonucleotides sensitize human ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis
- PMID: 23634944
- PMCID: PMC3660071
- DOI: 10.1089/nat.2012.0401
Telomere-homologous G-rich oligonucleotides sensitize human ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis
Abstract
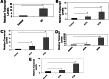
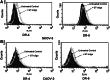
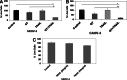
G-rich T-oligos (GT-oligos; oligonucleotides with homology to telomeres) elicit a DNA damage response in cells and induce cytotoxic effects in certain tumor cell lines. We have previously shown that GT-oligo inhibits growth, arrests cell cycle, and induces apoptosis in ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancer cells. However, not all ovarian cancer cell lines are susceptible to GT-oligo exposure. GT-oligo was found to induce transcript expression of the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptors DR-4 and DR-5, which are generally silenced in ovarian cancer cells, rendering them insensitive to TRAIL. Exposure of TRAIL- and GT-oligo-resistant cell lines to GT-oligo rendered them sensitive to the cytotoxic effects of TRAIL, producing more than additive inhibition of growth. An intracellular inhibitor of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway, FLICE-like Inhibitory Protein-Short (FLIPs), was down-regulated and Jun kinase (JNK) was activated by exposure to GT-oligo. JNK inhibition partially reversed the growth inhibition caused by the combination of GT-oligo and TRAIL indicating partial involvement of the Jun kinase pathway in the resulting cytotoxic effect. Both capase-8 and caspases 3/7 were activated by exposure to GT-oligo plus TRAIL, consistent with activation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. These results demonstrate a novel way of sensitizing resistant ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated cytotoxicity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High susceptibility of metastatic cells derived from human prostate and colon cancer cells to TRAIL and sensitization of TRAIL-insensitive primary cells to TRAIL by 4,5-dimethoxy-2-nitrobenzaldehyde.Mol Cancer. 2011 Apr 25;10:46. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-46. Mol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21513580 Free PMC article.
-
Human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells express TRAIL receptors and can be sensitized to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.Stem Cells Dev. 2013 Nov 15;22(22):2964-74. doi: 10.1089/scd.2013.0057. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Stem Cells Dev. 2013. PMID: 23806100 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of cFLIP following reovirus infection sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis.Apoptosis. 2007 Jan;12(1):211-23. doi: 10.1007/s10495-006-0528-4. Apoptosis. 2007. PMID: 17136319 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins, particularly c-FLIP by therapeutic agents; the novel view to overcome resistance to TRAIL.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6470-6485. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26585. Epub 2018 May 9. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29741767 Review.
-
Regulation of Cancer Metastasis by TRAIL/Death Receptor Signaling.Biomolecules. 2021 Mar 26;11(4):499. doi: 10.3390/biom11040499. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33810241 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Telomeres and Telomere Length: A General Overview.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 28;12(3):558. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030558. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32121056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treating Cancer by Targeting Telomeres and Telomerase.Antioxidants (Basel). 2017 Feb 19;6(1):15. doi: 10.3390/antiox6010015. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28218725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug resistance in cancer: an overview.Cancers (Basel). 2014 Sep 5;6(3):1769-92. doi: 10.3390/cancers6031769. Cancers (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25198391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of therapies-mediated modulation of telomere and/or telomerase on cancer cells radiosensitivity.Oncotarget. 2018 Oct 9;9(79):35008-35025. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26150. eCollection 2018 Oct 9. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30405890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensitization of Drug Resistant Cancer Cells: A Matter of Combination Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Dec 4;10(12):483. doi: 10.3390/cancers10120483. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30518036 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- BAE S.I. CHERIYATH V. JACOBS B.S. REU F.J. BORDEN E.C. Reversal of methylation silencing of Apo2L/TRAIL receptor 1 (DR4) expression overcomes resistance of SK-MEL-3 and SK-MEL-28 melanoma cells to interferons (IFNs) or Apo2L/TRAIL. Oncogene. 2008;27:490–498. - PubMed
-
- CAMIDGE D.R. Apomab: an agonist monoclonal antibody directed against Death Receptor 5/TRAIL-Receptor 2 for use in the treatment of solid tumors. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2008;8:1167–1176. - PubMed
-
- CHAWLA-SARKAR M. BAE S.I. REU F.J. JACOBS B.S. LINDNER D.J. BORDEN E.C. Downregulation of Bcl-2, FLIP or IAPs (XIAP and survivin) by siRNAs sensitizes resistant melanoma cells to Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2004;11:915–923. - PubMed
-
- CUMMINS J.M. KOHLI M. RAGO C. KINZLER K.W. VOGELSTEIN B. ND BUNZ F. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) is a nonredundant modulator of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3006–3008. - PubMed
-
- DUIKER E.W. DE VRIES E.G. MAHALINGAM D. MEERSMA G.J. BOERSMA-VAN EK W. HOLLEMA H. LUB-DE HOOGE M.N. VAN DAM G.M. COOL R.H. QUAX W.J., et al. Enhanced antitumor efficacy of a DR5-specific TRAIL variant over recombinant human TRAIL in a bioluminescent ovarian cancer xenograft model. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009;15:2048–2057. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

