A four-way, double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled study to determine the efficacy and speed of azelastine nasal spray, versus loratadine, and cetirizine in adult subjects with allergen-induced seasonal allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 23635091
- PMCID: PMC3655060
- DOI: 10.1186/1710-1492-9-16
A four-way, double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled study to determine the efficacy and speed of azelastine nasal spray, versus loratadine, and cetirizine in adult subjects with allergen-induced seasonal allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Background: Azelastine has been shown to be effective against seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR). The Environmental Exposure Unit (EEU) is a validated model of experimental SAR. The objective of this double-blind, four-way crossover study was to evaluate the onset of action of azelastine nasal spray, versus the oral antihistamines loratadine 10 mg and cetirizine 10 mg in the relief of the symptoms of SAR.
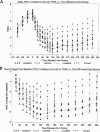
Methods: 70 participants, aged 18-65, were randomized to receive azelastine nasal spray, cetirizine, loratadine, or placebo after controlled ragweed pollen exposure in the EEU. Symptoms were evaluated using the total nasal symptom score (TNSS). The primary efficacy parameter was the onset of action as measured by the change from baseline in TNSS.
Results: Azelastine displayed a statistically significant improvement in TNSS compared with placebo at all time points from 15 minutes through 6 hours post dose. Azelastine, cetirizine, and loratadine reduced TNSS compared to placebo with an onset of action of 15 (p < 0.001), 60 (p = 0.015), and 75 (p = 0.034) minutes, respectively. The overall assessment of efficacy was rated as good or very good by 46% of the participants for azelastine, 51% of the participants for cetirizine, and 30% of the participants for loratadine compared to 18% of the participants for placebo.
Conclusions: Azelastine's onset of action for symptom relief was faster than that of cetirizine and loratadine. The overall participant satisfaction in treatment with azelastine is comparable to cetirizine and statistically superior to loratadine. These results suggest that azelastine may be preferential to oral antihistamines for the rapid relief of SAR symptoms.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; Azelastine; Cetirizine; Environmental exposure unit; Loratadine; Onset of action.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

