A real-time regional adaptive exposure method for saving dose-area product in x-ray fluoroscopy
- PMID: 23635281
- PMCID: PMC3651207
- DOI: 10.1118/1.4801908
A real-time regional adaptive exposure method for saving dose-area product in x-ray fluoroscopy
Abstract
Purpose: Reduction of radiation dose in x-ray imaging has been recognized as a high priority in the medical community. Here the authors show that a regional adaptive exposure method can reduce dose-area product (DAP) in x-ray fluoroscopy. The authors' method is particularly geared toward providing dose savings for the pediatric population.
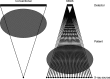
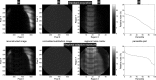
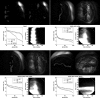
Methods: The scanning beam digital x-ray system uses a large-area x-ray source with 8000 focal spots in combination with a small photon-counting detector. An imaging frame is obtained by acquiring and reconstructing up to 8000 detector images, each viewing only a small portion of the patient. Regional adaptive exposure was implemented by varying the exposure of the detector images depending on the local opacity of the object. A family of phantoms ranging in size from infant to obese adult was imaged in anteroposterior view with and without adaptive exposure. The DAP delivered to each phantom was measured in each case, and noise performance was compared by generating noise arrays to represent regional noise in the images. These noise arrays were generated by dividing the image into regions of about 6 mm(2), calculating the relative noise in each region, and placing the relative noise value of each region in a one-dimensional array (noise array) sorted from highest to lowest. Dose-area product savings were calculated as the difference between the ratio of DAP with adaptive exposure to DAP without adaptive exposure. The authors modified this value by a correction factor that matches the noise arrays where relative noise is the highest to report a final dose-area product savings.
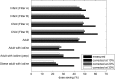
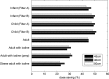
Results: The average dose-area product saving across the phantom family was (42 ± 8)% with the highest dose-area product saving in the child-sized phantom (50%) and the lowest in the phantom mimicking an obese adult (23%).
Conclusions: Phantom measurements indicate that a regional adaptive exposure method can produce large DAP savings without compromising the noise performance in the image regions with highest noise.
Figures



Similar articles
-
X-ray dose reduction through adaptive exposure in fluoroscopic imaging.J Vis Exp. 2011 Sep 11;(55):3236. doi: 10.3791/3236. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21931295 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation dose and image quality of X-ray volume imaging systems: cone-beam computed tomography, digital subtraction angiography and digital fluoroscopy.Eur Radiol. 2013 Jun;23(6):1582-93. doi: 10.1007/s00330-012-2737-2. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Eur Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23250112
-
Characterization of adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction algorithm for dose reduction in CT: A pediatric oncology perspective.Med Phys. 2012 Sep;39(9):5520-31. doi: 10.1118/1.4745563. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22957619
-
The impact of the fluoroscopic view on radiation exposure in pelvic surgery: organ involvement, effective dose and the misleading concept of only measuring fluoroscopy time or the dose area product.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022 Oct;32(7):1399-1405. doi: 10.1007/s00590-021-03111-z. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 34553249
-
Effect of x-ray tube parameters and iodine concentration on image quality and radiation dose in cerebral pediatric and adult CT angiography: a phantom study.Invest Radiol. 2013 Apr;48(4):192-9. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0b013e31827efc17. Invest Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23344518
Cited by
-
Method for dose-reduced 3D catheter tracking on a scanning-beam digital x-ray system using dynamic electronic collimation.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2016 Feb 27;9783:97831Y. doi: 10.1117/12.2216892. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2016. PMID: 27375314 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrahedron beam imaging with a multi-pixel thermionic emission X-ray source and a photon-counting detector: A benchtop experimental study.Med Phys. 2021 Nov;48(11):7250-7260. doi: 10.1002/mp.15211. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34482562 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-guided techniques for managing length- unstable femoral shaft fractures in children.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Aug 5;25(1):622. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07740-3. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39103800 Free PMC article.
-
Monte Carlo simulation of inverse geometry x-ray fluoroscopy using a modified MC-GPU framework.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2015 Feb 21;9412:94120S. doi: 10.1117/12.2081684. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2015. PMID: 26113765 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic electronic collimation method for 3-D catheter tracking on a scanning-beam digital x-ray system.J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2017 Apr;4(2):023501. doi: 10.1117/1.JMI.4.2.023501. Epub 2017 Apr 18. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 2017. PMID: 28439521 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

