Protein-protein interaction networks: probing disease mechanisms using model systems
- PMID: 23635424
- PMCID: PMC3706760
- DOI: 10.1186/gm441
Protein-protein interaction networks: probing disease mechanisms using model systems
Abstract
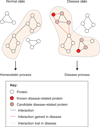
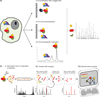
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) and multi-protein complexes perform central roles in the cellular systems of all living organisms. In humans, disruptions of the normal patterns of PPIs and protein complexes can be causative or indicative of a disease state. Recent developments in the biological applications of mass spectrometry (MS)-based proteomics have expanded the horizon for the application of systematic large-scale mapping of physical interactions to probe disease mechanisms. In this review, we examine the application of MS-based approaches for the experimental analysis of PPI networks and protein complexes, focusing on the different model systems (including human cells) used to study the molecular basis of common diseases such as cancer, cardiomyopathies, diabetes, microbial infections, and genetic and neurodegenerative disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Venkatesan K, Rual JF, Vazquez A, Stelzl U, Lemmens I, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Hao T, Zenkner M, Xin X, Goh KI, Yildirim MA, Simonis N, Heinzmann K, Gebreab F, Sahalie JM, Cevik S, Simon C, de Smet AS, Dann E, Smolyar A, Vinayagam A, Yu H, Szeto D, Borick H, Dricot A, Klitgord N, Murray RR, Lin C, Lalowski M, Timm J. et al.An empirical framework for binary interactome mapping. Nat Methods. 2009;6:83–90. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1280. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

