Mesenchymal stem cell mechanobiology and emerging experimental platforms
- PMID: 23635493
- PMCID: PMC3673151
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2013.0179
Mesenchymal stem cell mechanobiology and emerging experimental platforms
Abstract
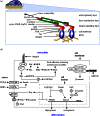
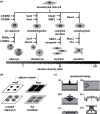
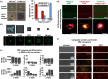
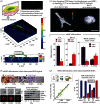
Experimental control over progenitor cell lineage specification can be achieved by modulating properties of the cell's microenvironment. These include physical properties of the cell adhesion substrate, such as rigidity, topography and deformation owing to dynamic mechanical forces. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) generate contractile forces to sense and remodel their extracellular microenvironments and thereby obtain information that directs broad aspects of MSC function, including lineage specification. Various physical factors are important regulators of MSC function, but improved understanding of MSC mechanobiology requires novel experimental platforms. Engineers are bridging this gap by developing tools to control mechanical factors with improved precision and throughput, thereby enabling biological investigation of mechanics-driven MSC function. In this review, we introduce MSC mechanobiology and review emerging cell culture platforms that enable new insights into mechanobiological control of MSCs. Our main goals are to provide engineers and microtechnology developers with an up-to-date description of MSC mechanobiology that is relevant to the design of experimental platforms and to introduce biologists to these emerging platforms.
Keywords: high-throughput screening; mechanobiology; mesenchymal stem cell; microfluidics; microtechnology; niche.
Figures



References
-
- Moore KA, Lemischka IR. 2006. Stem cells and their niches. Science 311, 1880–188510.1126/science.1110542 (doi:10.1126/science.1110542) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yin T, Li LH. 2006. The stem cell niches in bone. J. Clin. Invest. 116, 1195–120110.1172/Jci28568 (doi:10.1172/Jci28568) - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ehninger A, Trumpp A. 2011. The bone marrow stem cell niche grows up: mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages move in. J. Exp. Med. 208, 421–42810.1084/Jem.20110132 (doi:10.1084/Jem.20110132) - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cosgrove BD, Sacco A, Gilbert PM, Blau HM. 2009. A home away from home: challenges and opportunities in engineering in vitro muscle satellite cell niches. Differentiation 78, 185–19410.1016/j.diff.2009.08.004 (doi:10.1016/j.diff.2009.08.004) - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Discher DE, Mooney DJ, Zandstra PW. 2009. Growth factors, matrices, and forces combine and control stem cells. Science 324, 1673–167710.1126/science.1171643 (doi:10.1126/science.1171643) - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

