The contextual brain: implications for fear conditioning, extinction and psychopathology
- PMID: 23635870
- PMCID: PMC5072129
- DOI: 10.1038/nrn3492
The contextual brain: implications for fear conditioning, extinction and psychopathology
Abstract
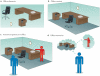
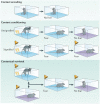
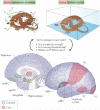
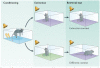
Contexts surround and imbue meaning to events; they are essential for recollecting the past, interpreting the present and anticipating the future. Indeed, the brain's capacity to contextualize information permits enormous cognitive and behavioural flexibility. Studies of Pavlovian fear conditioning and extinction in rodents and humans suggest that a neural circuit including the hippocampus, amygdala and medial prefrontal cortex is involved in the learning and memory processes that enable context-dependent behaviour. Dysfunction in this network may be involved in several forms of psychopathology, including post-traumatic stress disorder, schizophrenia and substance abuse disorders.
Figures
References
-
- Spear N. Retrieval of memory in animals. Psychol. Rev. 1973;80:194.
-
- Bouton M. Context, time, and memory retrieval in the interference paradigms of Pavlovian learning. Psychol. Bull. 1993;114:99. - PubMed
-
- Bouton M. Context, ambiguity, and classical conditioning. Curr. Direct. Psychol. Sci. 1994;3:53.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

